Figure 6.
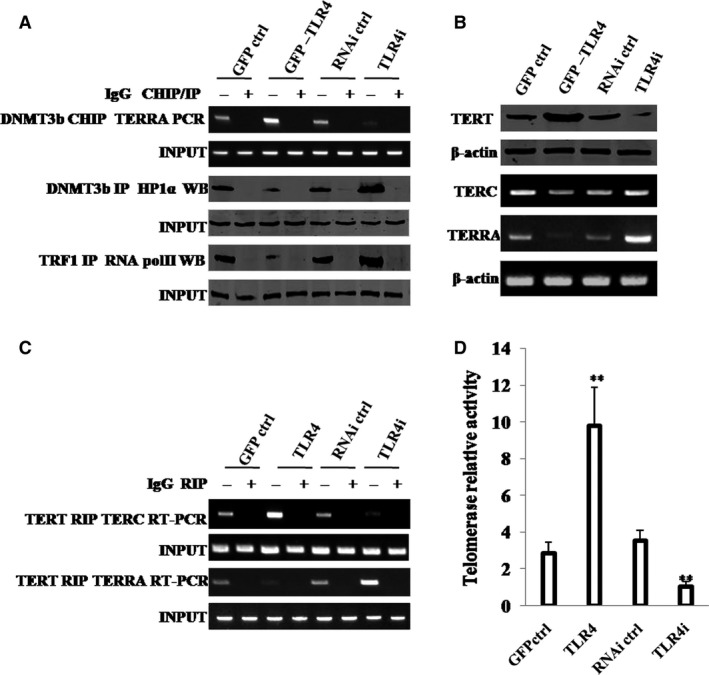
TLR4 increases telomerase activity through HP1α‐DNMT3b. A, (upper) ChIP assay with anti‐DNMT3b followed by PCR with TERRA promoter primers. IgG ChIP served as negative control. PCR with TERRA promoter served as INPUT. (middle) Co‐IP with anti‐DNMT3b followed by Western blotting with anti‐HP1α. IgG IP served as negative control. Western blotting with anti‐HP1α served as INPUT. (lower) Co‐IP with anti‐TRF1 followed by Western blotting with anti‐RNA polII. IgG IP served as negative control. Western blotting with anti‐RNA polII served as INPUT. B, (upper) Western blotting with anti‐TERT. (lower) RT‐PCR with TERC and TERRA primers for four hLCSC lines. β‐Actin served as internal control. C, RIP with anti‐TERT followed by RT‐PCR with TERC and TERRA primers. IgG RIP served as negative control. RT‐PCR for TERC or TERRA served as INPUT. D, Telomerase assay with TRAP method. Each value was presented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). Bar ± SEM. **P < .01; *P < .05. For all Western blotting, we repeated the experiments for three times. We measured grey value of the bands for quantification. Each value was presented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) (Student's t test)
