Figure 8.
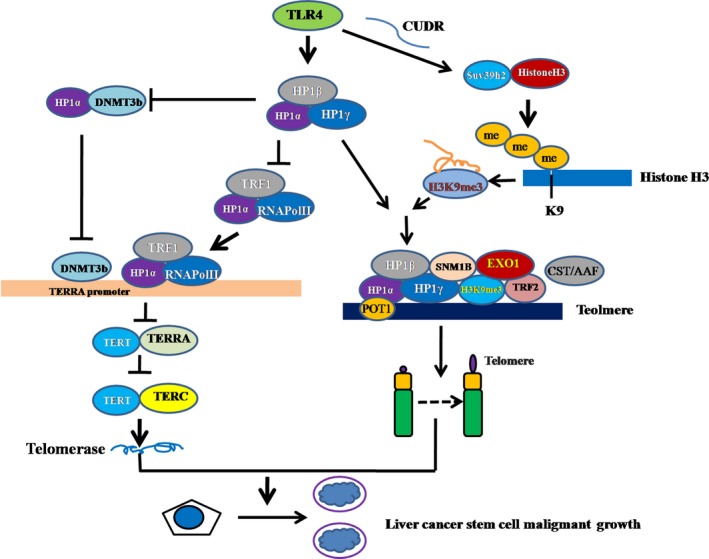
Schematic illustration of the role of TLR4 in malignant proliferation and growth of hLCSCs in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, TLR4 promotes expression of SUV39 h2 (which methylates H3K9 to form H3K9me3) and then increases formation of H3K9me3‐HP1‐TRF2 complex at the telomeric locus under mediation by long non coding CUDR. At the telomeric locus, this complex promotes binding of POT1, pPOT1, Exo1, pExo1, SNM1B and pSNM1B but prevents binding of CST/AAF to telomere, thus controlling telomere and maintaining telomere length. Furthermore, TLR4 inhibits the interaction between HP1α and DNMT3b, which limits RNA polymerase II deposition on TERRA promoter region and its elongation, thus inhibiting transcription of TERRA. Ultimately, TLR4 enhances the telomerase activity by reducing interplay between TERT and TERRA but enhancing the interplay between TERT and TERC
