Figure 2.
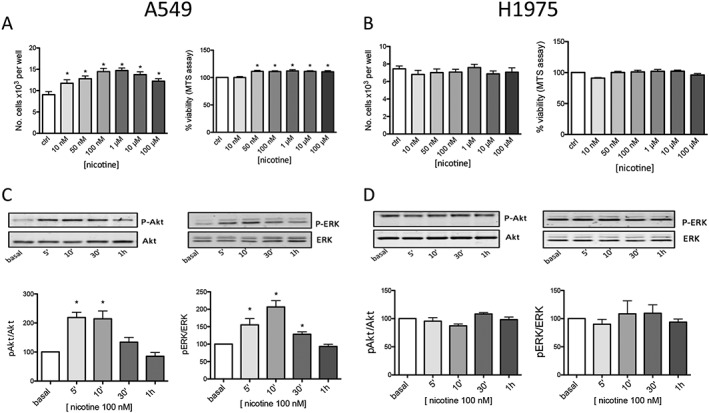
Effects of chronic nicotine exposure on A549 and H1975 cell viability, proliferation and signalling. (A, B) Chronic (48 h) exposure to the indicated concentrations of nicotine increased A549 cells viability and number of A549 (A) but not H1975 (B) cells. Results are the average of eight proliferation and viability experiments for A549 and H1975 cells performed in triplicate. The analysis was made using one‐way ANOVA followed by a post hoc Bonferroni test (cell count) or Dunn's test (cell viability) (*P < 0.05). A549 (C) and H1975 (D) cells were treated with 100 nM nicotine for the indicated times, and the incubation was blocked by adding sample buffer. Proteins were separated on 9% acrylamide SDS gels, transferred to nitrocellulose and probed with Abs directed against Akt and p‐Akt ERK and p‐ERK as described in Methods. The Western blot results are expressed as the p‐Akt/Akt and p‐ERK/ERK ratios, taking the ratio of control samples as 100 at the indicated time of nicotine stimulation (0, 5, 10, 30 and 60 min). The graphs show the mean values ±SEM obtained in eight different experiments performed in duplicate or triplicate. A representative blot at the corresponding times is shown above the graph. The Western blotting data were statistically analysed using one‐way ANOVA followed by Dunn's test [*P < 0.05 vs. untreated (basal) cells].
