Figure 6.
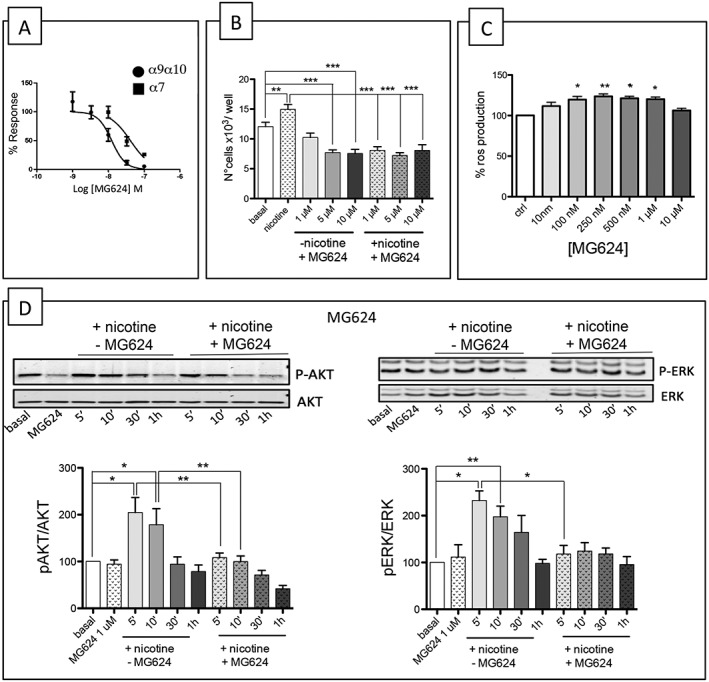
Characterization of the effect of MG624. (A) Effects of MG624 on Xenopus oocytes expressing α9–α10‐ and α7‐containing nicotinic receptors. Oocytes were injected with mRNA encoding the human α9–α10 or α7 subunits. Concentration–effect curves of MG624 inhibition of ACh‐induced ion currents. Within each group, all responses were normalized to an initial control stimulation (see Methods). The data points represent mean values ±SEM. Drug potency and efficacy parameters were calculated using nonlinear least‐squares curve fitting to the Hill equation. (B) MG624 decreases A549 proliferation. MG624 (1, 5 and 10 μM) abolished the chronic (48 h) nicotine‐induced increase in the number of A549 cells (n = 5). The analysis was made using one‐way ANOVA followed by a post hoc Bonferroni's test (cell count) (*P < 0.05). (C) MG624 increases ROS production. A549 cells were seeded in black 96‐well plates, pretreated with the indicated concentrations of MG624 for 24 h and then incubated with 25 μM DCFH‐DA for 30 min at 37°C. Fluorescence was measured at 485 nmex/530 nmem using a microplate reader. The results are expressed as the increase in fluorescence units·mg−1 of cell proteins taking the production of ROS in untreated cells as 100%. The analysis was made using one‐way ANOVA followed Dunn's test (*P < 0.05). (D) MG624 blocks the nicotine‐induced activation of p‐ERK and p‐Akt. Western blot analysis of ERK and Akt pathway activation upon nicotine stimulation in A549 cells with or without MG624 (1 μM) (n = 5).
