Figure 2.
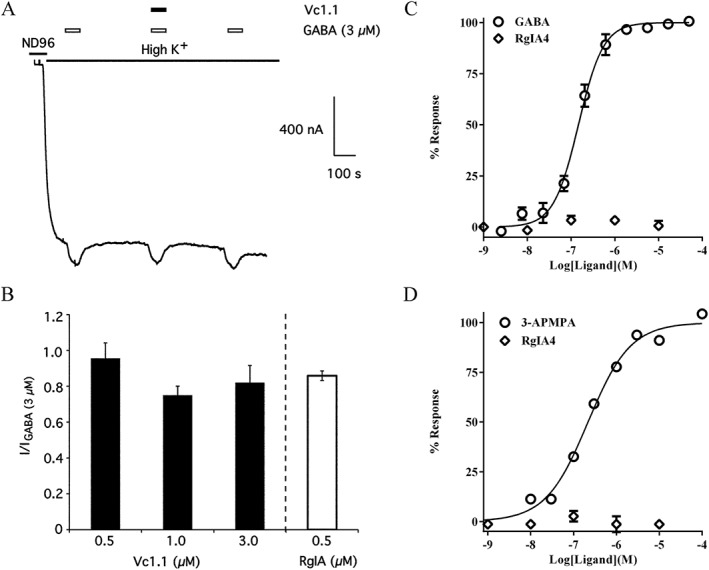
Analgesic α‐Ctxs Vc1.1, RgIA and RgIA4 fail to activate heterologously expressed GABAB receptors. α‐Ctxs have not shown agonist activity in a variety of functional assays designed to measure GABAB receptor activity. (A) Vc1.1 failed to activate human GABAB receptors functionally coupled to Kir (GIRK) channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes. The oocytes were stimulated with 45 mM K+ and then pulsed with GABA or GABA + Vc1.1 to stimulate GABAB receptor activation of Kir channels. Note that GABA, but not Vc1.1, increased K+ currents. Similar results were obtained with RgIA in the same assay. (B) Histogram showing the lack of effect of Vc1.1 and RgIA on Kir channel activation. (figures in A and B were used with permission of McIntosh et al., 2009). (C) Gi‐coupled cAMP modulation was assessed in CHO cells expressing GABAB1a/B2 receptors with Gi/o coupling. GABA produced an increase in cAMP response in a concentration‐dependent manner, whereas RgIA4 had no effect at any of the concentrations tested. (D) Cellular dielectric spectroscopy was used to assay changes in electrical impedance using CHO cells expressing human GABAB1a/B2 receptors during stimulation with the GABAB receptor agonist 3‐aminopropyl(methyl)phosphonic acid (3‐AMPA). 3‐AMPA produced changes in cellular impedance in a concentration‐dependent manner, whereas RgIA4 had no effect. (Figures in C and D were used with the permission of Romero et al., 2017).
