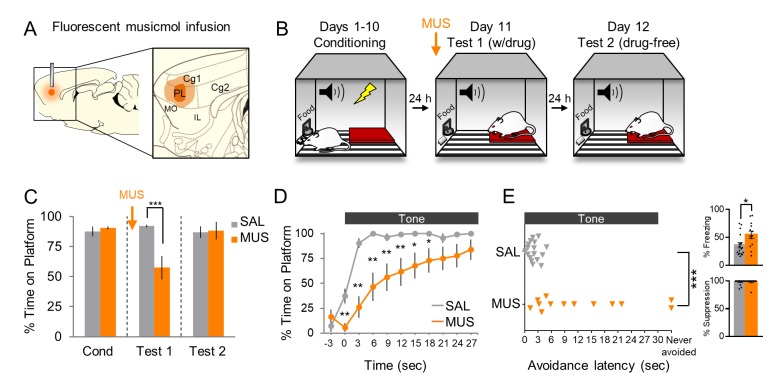
Figure 1. Pharmacological inactivation of prelimbic cortex delays avoidance.
(A). Schematic of MUS infusion showing the minimum (dark orange) and maximum (light orange) extent of infusion into PL. (B). Rats were trained across 10 days to avoid a tone-signaled foot-shock by stepping onto a platform. On Day 11, rats received two tone presentations (without shock) 45 min after MUS infusion. On Day 12, rats received a second 2-tone test drug free. (C). Percent time on platform during Tone 1 on Days 10, 11, and 12 for MUS and saline controls (SAL, n = 17; grey) and MUS rats (n = 13, orange). (D). Time spent on platform in 3 s bins for Test 1 (Tone 1) revealed that MUS rats were significantly delayed in their avoidance compared to SAL controls (repeated measures ANOVA, post hoc Tukey). (E). Latency of avoidance for each rat (Mann Whitney U test, Tone 1, Test 1). Inset: Effect of MUS inactivation (Tone 1, test 1) on freezing (top) and percent suppression of bar pressing (bottom) during the tone (unpaired t-test). Data are shown as mean ± SEM; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
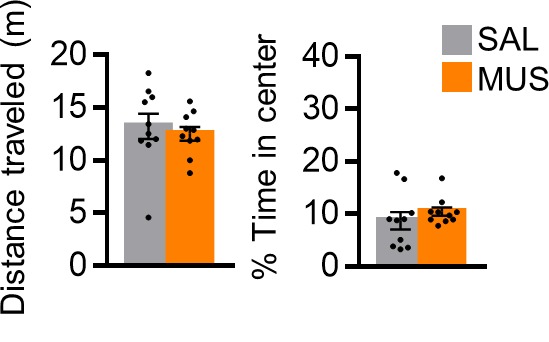
Figure 1—figure supplement 1. Assessment of locomotion and anxiety following pharmacological inactivation of PL.