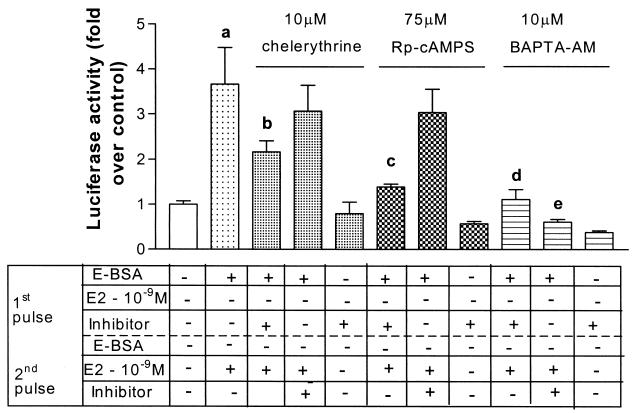
Figure 3.
Inhibitors of PKA, PKC, and Ca2+ release, block the ability of E-BSA in the first pulse to potentiate transactivation. SK-N-BE2C cells were treated as described in Fig. 1A. Chelerythrine (PKC inhibitor), Rp-cAMPS (PKA inhibitor), and BAPTA-AM (a calcium chelator) were coadministered with 10−9 M E-BSA in the first 2-h pulse (third, sixth, and ninth bars from the left, respectively) at the concentrations detailed above. They were also coadministered with 10−9 M 17β-estradiol in the second 2-h pulse (fourth, seventh, and tenth bars from the left) or given alone in the first 2-h pulse (fifth, eight, and eleventh bars from the left). Results, plotted as fold over control, represent mean + SEM (n = 8 per treatment group from replicate experiments). Statistical analysis was done by using one-way ANOVA, using Student Newman Keuls post hoc test to compare between treatment groups. a, P < 0.001 compared with vehicle treatment. b, P < 0.01 compared with E-BSA given in the first pulse followed by 17β-estradiol in the second pulse. c, d, and e, P < 0.001 compared with E-BSA given in the first pulse followed by 17β-estradiol in the second pulse.