Figure 2.
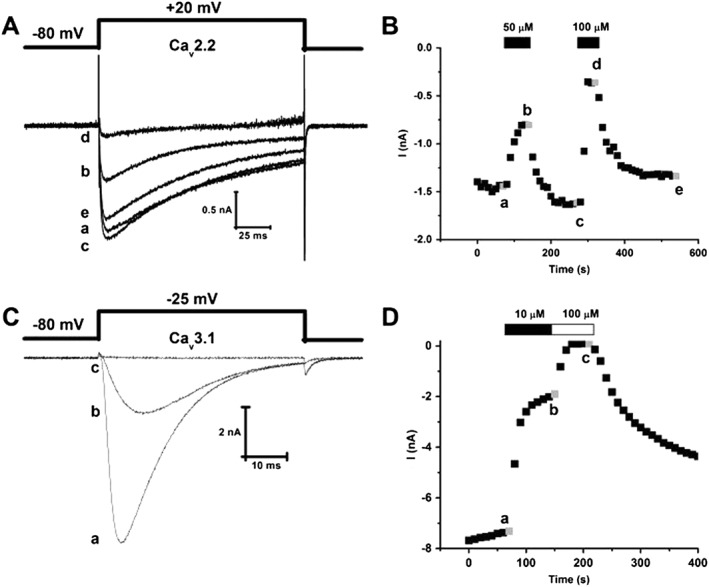
MONIRO‐1 inhibition of human Cav2.2‐ and Cav3.1‐mediated currents in HEK293 cells. (A) Superimposed whole‐cell Ca2+ currents recorded from HEK293 cells stably expressing human N‐type calcium (hCav2.2) channels (α1B + β3 + α2δ1) in response to depolarizing pulses (135 ms duration) to +20 mV from a holding potential of −80 mV. Representative current traces obtained in the absence (a) and presence of 50 (b) and 100 μM (d) MONIRO‐1 and after respective washouts (c, e). (B) Peak inward Ca2+ current amplitude plotted as a function of time. Time course of inhibition and current amplitude recovery in the presence and following washout of 50 and 100 μM MONIRO‐1. Representative currents shown in (A) were obtained at the times indicated by the lower case letters. (C) Superimposed whole‐cell Ca2+ currents recorded from HEK293 cells transiently expressing human T‐type calcium channel, hCav3.1. These Ca2+ currents are in response to depolarizing pulses (50 ms duration) to −25 mV from a holding potential of −80 mV. Representative current traces obtained in the absence (a) and presence of 10 μM (b) and 100 μM (c) MONIRO‐1. (D) Peak inward Ca2+ current amplitude plotted as a function of time. Time course of inhibition and recovery of current amplitude in the absence (a) and presence of 10 (b) and 100 μM (c) MONIRO‐1.
