Table 1.
Synopsis of functional properties and pharmacology of the P2X ATP‐gated channels involved in nociception and chronic pain. Calcium permeability of P2X receptor subtypes is indicated in fractional current (data from Egan and Khakh, 2004). The selective antagonists in bold typeface are displayed in Figure 3.
| Subtype | P2X3 | P2X2/3 | P2X4 | P2X7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current phenotype |

|
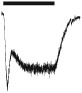
|

|

|
| Calcium permeability (%) | 2.7 (rat) | 3.5 (rat) | 15 (human) | 4.6 (rat) |
| Large pore | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Link to pannexin | No | No | No | Yes |
| Agonists | ATP, αβ‐meATP, 2‐MeS‐ATP, BzATP and Ap(n)A | As for the P2X3 homomer | ATP > BzATP, 2‐MeS‐ATP, AP4, γ‐S‐ATP and αβ‐meATP | BzATP > ATP, 2‐MeS‐ATP and αβ‐meATP |
| Antagonists | Suramin, PPADS, TNP‐ATP, Ap4A analogs, A317491, RO‐3, AF‐219, RO‐51, AF‐353, AF‐906, NF279, MK‐3901, MRS 3357, Tricyclics, 5‐OH‐pyridines and 3,4‐dicarboxy‐pyridines | As for the P2X3 homomer | PPADS, paroxetine, duloxetine, 5‐BDBD, PSB‐12054, PSB‐12062, CORM‐2, carbamazepines, artemisinin, NP‐1815‐PX and BX430 | PPADS, BBG, oATP, decavanadate, KN62, NF279, A‐740003, A438079, A804598, A839977, AZ10606120, AZ11645373, GW791343, AZD9056, GSK1482160, GSK314181A, CE‐224535, JNJ‐479655, pyrimidine‐2,4‐diones, ZINC09315614, chloro‐purines, RO‐3, AF‐353, AF‐906, acetamides, 3,5‐DiCl‐pyridines, protoberberines, pyrazol‐acetamides, cyanoguanidines, teniposide, tanshinone IIAS, methanones, nanoAb 13A7 and nanoAb Dano1 |
| Selective for P2X3 homomers: IP5I, AZ004, RO‐85, mAb 12D4 and spinorphin | ||||
| Cellular distribution (pain‐related) | Primary sensory neurons (dorsal root, nodose and trigeminal ganglia) | As for the P2X3 homomer | CNS neurons, monocytes, macrophages and microglia | Lymphocytes, monocytes, macrophages, microglia, CNS neurons and astrocytes |
