Figure 3.
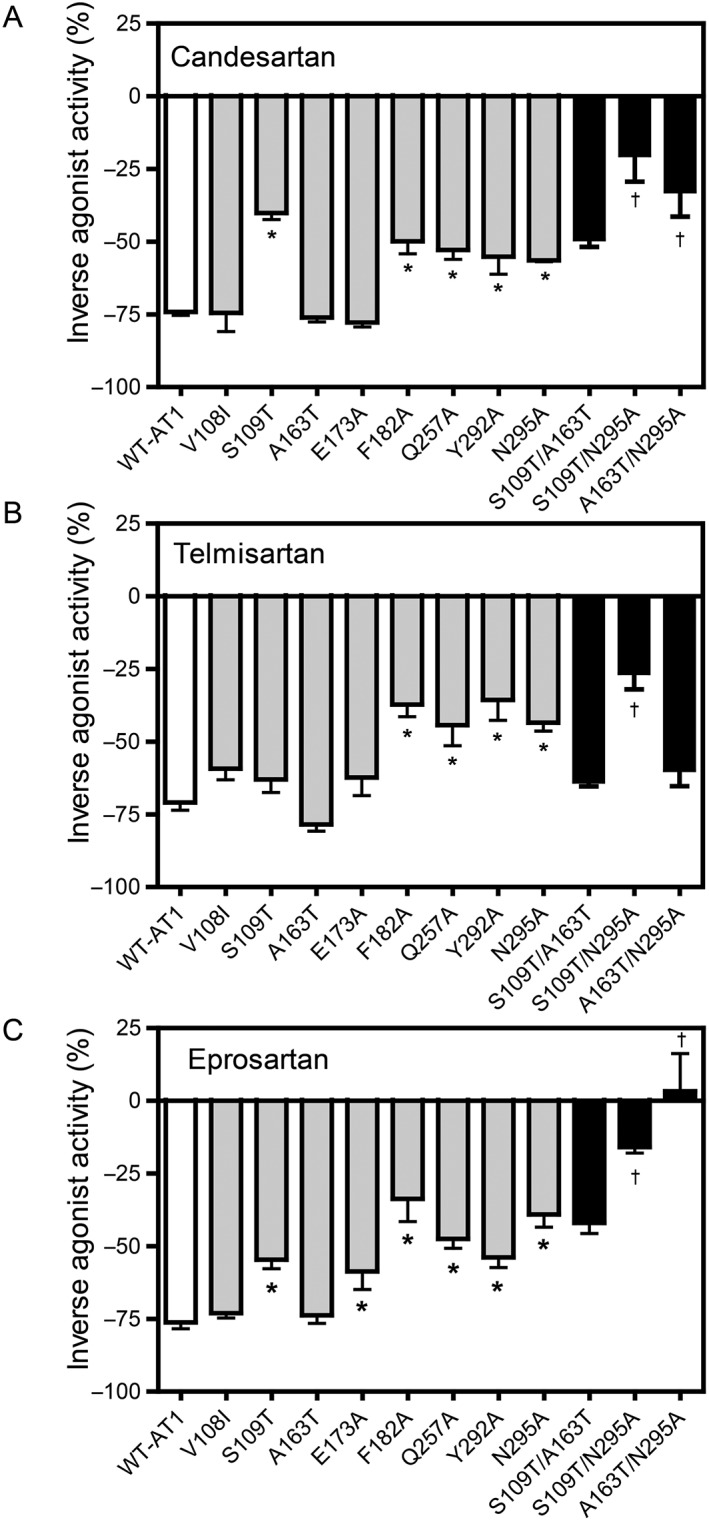
Effects of the AT1 receptor mutants on the inverse agonist activities of candesartan, telmisartan and eprosartan in cells expressing various mutants of WT‐AT1 receptors, as measured by the IP assay. The inverse agonist activities of (A) candesartan, (B) telmisartan and (C) eprosartan at a concentration of 10 μM for each ARB in COS‐1 cells transfected with WT‐AT1 receptors, single mutants and double mutants are shown. The double mutants were constructed using two independent mutants that significantly attenuated the inverse agonist activity. The inverse agonist activities are expressed as a percentage of the constitutive activity of either WT‐AT1 receptors or each mutant. The constitutive activities of the vehicle‐treated cells expressing WT‐AT1 receptors and each mutant were defined as 0% for each. Data represent mean ± SEM of independent experiments [candesartan: n = 8 (WT‐AT1 receptor) and n = 6 (all mutants); telmisartan: n = 12 (Y292A), n = 10 (WT‐ AT1 receptor, E173A and Q257A), n = 8 (N295A) and n = 6 (all other mutants); and eprosartan: n = 12 (WT‐ AT1 receptor), n = 10 (E173A, Q257A, Y292A and N295A) and n = 6 (all other mutants)]. Group sizes are not equal in Figure 3. The reason for this is that data of some groups showed large SEM when n = 6 per group, and we had to examine additional experiments to confirm exact value for these groups. * P < 0.05, significant difference from WT‐ AT1 receptors †, additive effect; one‐way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's or Dunnett's post hoc tests.
