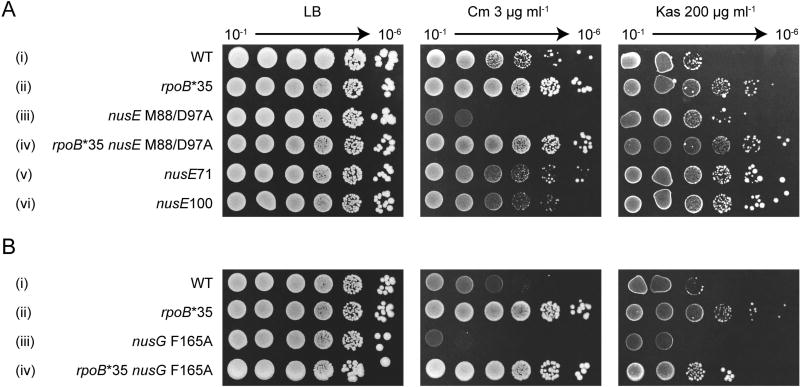
Figure 4. Mutations in the NusG:ribosome interface affect transcription-translation coupling in vivo.
Colony-forming ability was assayed in the presence of 3 µg ml−1 chloramphenicol (Cm) targeting translation elongation and 200 µg ml−1 kasugamycin (Kas) targeting translation initiation. (A) The effect of nusE M88/D97A and other S10 mutations on strain growth in the presence of antibiotics. In every strain the nusE gene is linked to tetracycline-resistant Tn10. The strain order from top to bottom: 10401, KM821, 11601, KM820, 10400, KM812. (B) The effect of nusG F165A mutation on strain growth in the presence of antibiotics targeting translation. In all strains the nusG gene is linked to a kanamycin resistance cassette. The order of strains from top to bottom: KM848, KM852, KM850, KM854.