Figure 5. Loss of Ptch1 reduces mesodermal allocation by preventing resolution of the EMT in the AX.
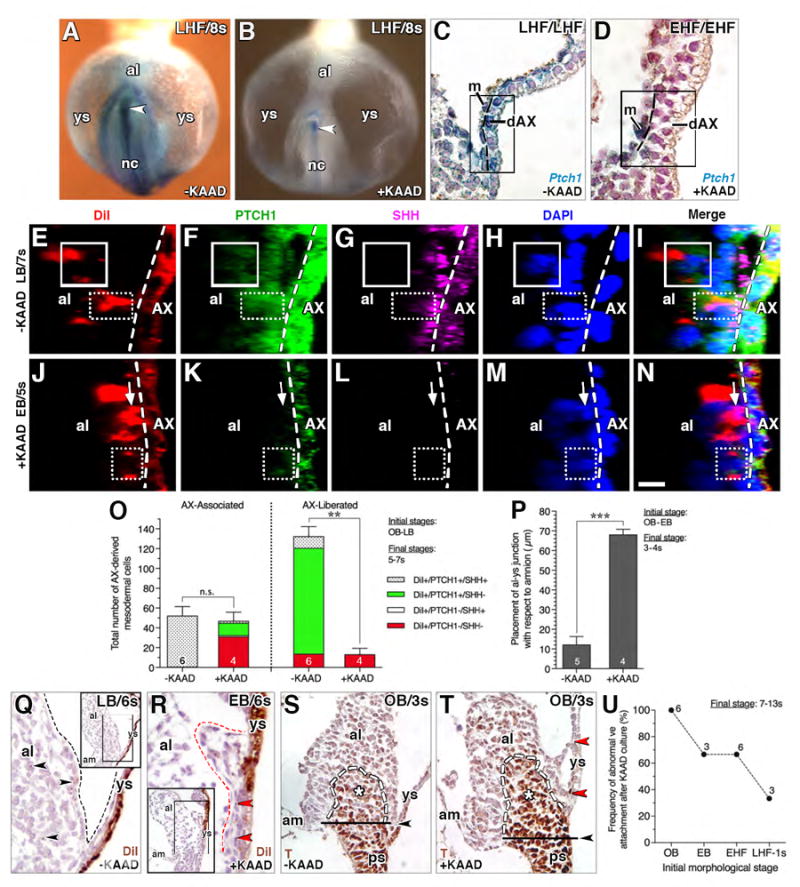
(A, B) Frontal (ventral) views, X-gal-stained whole mount Ptch1:lacZ reporter conceptuses after culture: A, untreated control (-KAAD), B, KAAD-cyclopamine-treated (+KAAD). Arrowhead, Ptch1 in posterior notochord. (C, D) Sagittal histological section, dAX, Ptch1:lacZ reporter conceptuses showing high Ptch1 in the untreated control (C), and loss of Ptch1 in dAX (D) after 4 hours of KAAD treatment. Boxed region, yolk sac mesothelium with residual Ptch1, and multilayering of the dAX, delineated by dashed line. (E-N) Sagittal slice, reconstructed z-stack, DiI labeled/AX-derived mesodermal cells (left of white dashed line, AX boundary) normally exhibit both SHH and PTCH1 when associated with AX (solid box, E-I) and only PTCH1 (dotted box, E-I) once liberated from AX; upon KAAD-treatment, AX-derived cells remain largely associated with AX, exhibiting only PTCH1 (dotted box, J-N) or neither PTCH1 or SHH (arrow). (O) Number of DiI-labeled AX-derived mesodermal cells in untreated and KAAD-treated specimens, categorized as AX-associated, i.e., in contact with the AX, and AX-liberated, i.e., fully disengaged from the AX. Mean ± SEM and sample sizes. Significance: Student t-Tests;: n.s., not significant with P = 0.623; **, P < 0.01. (P) Placement of allantoic-yolk sac junction with respect to amnion in -KAAD and +KAAD specimens; mean ± SEM and sample sizes. Significance: Student t-Tests; ***, P < 0.001. (Q, R) Sagittal histological sections, DiI-photobleached allantois KAAD-treated initially at bud stages and cultured through 6s. These compare normal tissue separation at the allantoic-yolk sac junction (black dashed line, Q) of untreated controls with the abnormal clumping between the allantois and yolk sac (red dashed line, R) after KAAD-treatment. Black arrowheads (Q), AX-derived cells fully liberated from the AX in the untreated specimens; red arrowhead (R), immobilized AX-derived cells that have not been liberated from the AX in the absence of Hedgehog. Main panels are enlargements of boxed region in insets. (S, T) Sagittal histological sections comparing untreated (S) and KAAD-treated (T) pre-bud (no allantoic bud, OB) conceptuses, both of which exhibit normal localization of T. Black arrowheads (S, T), correct placement of allantoic-yolk sac junction (S) and where it should have been in the KAAD-treated specimens (T). Red arrowheads (T), abnormal connections between the dAX and allantois. (U) Frequency of abnormal visceral endoderm (ve) attachments after KAAD culture at increasing initial morphological stages, with sample sizes. Scale bar (N): 10 μm (E-N); 18 μm (C, D); 35 μm (Q, R); 40 μm (S, T); 100 μm (A, B). al, allantois; am, amnion; m, mesothelium; nc, notochord; ps, primitive streak; ys, yolk sac.
