Figure 6. Abnormal structural organization of the fetal-placental interface in the absence of Hedgehog.
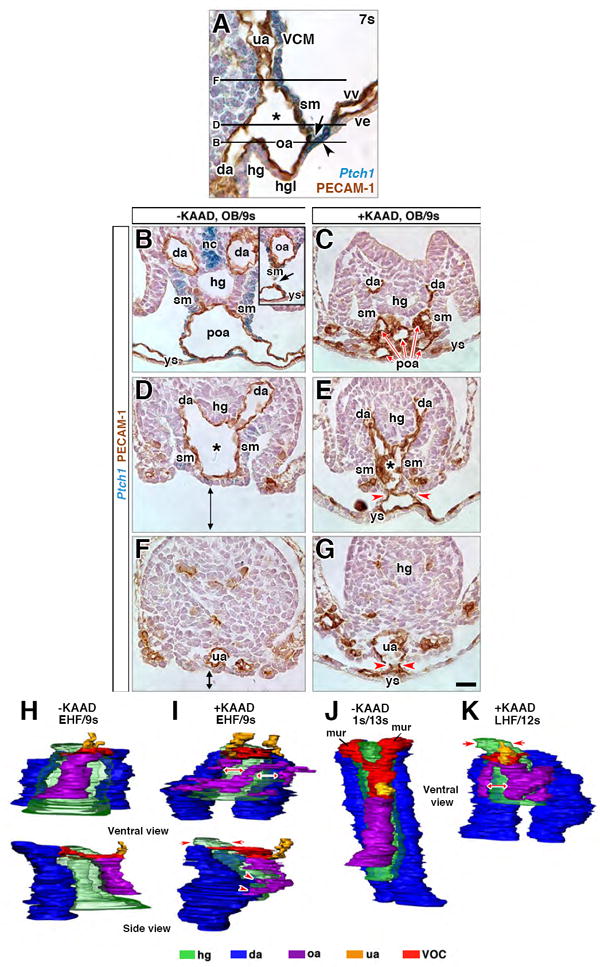
(A) Sagittal PECAM-1-immunostained histological section, fetal-placental interface, 7s-stage Ptch1:lacZ reporter conceptus. The allantoic-yolk sac junction is defined by the dAX (black arrowhead) and splanchnic mesoderm (sm; black arrow) continuous with the ventral allantoic wall (VCM). High Ptch1 localizes to VCM, sm, and dAX. The umbilical artery (ua), omphalomesenteric artery (oa), and dorsal aortae (da) have united at the vessel of confluence (asterisk). The hindgut lip (hgl) expresses relatively low Ptch1. Horizontal lines indicate the planes of section illustrated in B-G. (B-G) Transverse PECAM-1-immunostained histological sections of untreated (-KAAD; B, D, F) and KAAD-treated (+KAAD; C, E, G) specimens, taken at the level equivalent to the lines indicated in A. Black arrow (B inset), site where omphalomesenteric artery is released from the vitelline vasculature. Red arrows (C), prospective omphalomesenteric artery (poa) presented as multiple vessels. Double arrows (D, F) indicate that vessel of confluence (D, black asterisk) and umbilical artery (ua, F) are separated from the vitelline vasculature in the untreated specimens. Red arrowheads (E, G) indicate that the vessel of confluence (asterisk, E) and ua (G) remain tethered to the vitelline vasculature in KAAD-treated specimens. (H-K) 3D models reconstructed from PECAM-1-immunostained arterial vessels and associated hindgut at the posterior embryonic-extraembryonic interface prior to (H-I) or during (J-K) early remodeling of the vessel of confluence. Color key indicated below panels. Red double arrows (I, K) indicate abnormal gaps between the multiple vessels that appear to comprise the “oa”; red arrowheads (I) are aberrant connections between the oa and dorsal aortae (da); red arrows (I, K) indicate abnormal positioning of the hindgut (hg) distal to the vessel of confluence. Scale bar (G): 18 μm (A); 25 μm (D-G); 30 μm (B, C). al, allantois; mur, medial umbilical roots; nc, notochord; vv, vitelline blood vessels; ys, yolk sac.
