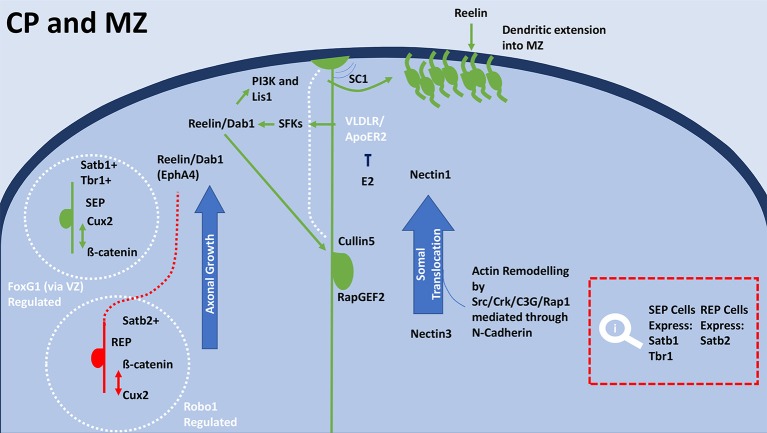
Figure 5.
General schematic of terminal translocation and differentiation in the CP during development. Within the CP SEP neurons (green) have high expression of Cux2 and low expression of β-catenin, whereas REP neurons (red) have high expression of β-catenin and low expression of Cux2. Satb1 positive cells express in the superficial layers of the MZ, which overlap with Tbr1 expression. Terminal translocation and therefore lamination rely on regulation by FoxG1 for the SEP neurons and radial distribution of Satb2 expressing REP neurons is regulated by Robo1. FoxG1 on deep-layer progenitors through transcription switches their progeny to upper-layer neurons through repression of Tbr1. After exiting the cell cycle, Satb2-expressing cells immediately migrate to the upper layers of the cortical plate. Satb2 expressing cells are much more reliant on the reelin/Dab1 and Ephrin-A pathways for cortical migration. Reelin binds to the RGCs by VLDLR and Apoer2 receptors (Lane-Donovan and Herz, 2017), which causes the adaptor protein Dab1 to become phosphorylated. Upon phosphorylation by SFKs, Dab1 recruits various downstream molecules including PI3K and Lis1. E2 is able to inhibit VLDLR/ApoER, modulates reelin's mechanisms in cortical migration. Reelin's interaction with cadherin is also essential for the termination of migration. Through regulating terminal translocation, the reelin/Dab1/Rap1/N-Cadherin signaling pathway leads to the inside-out lamination of the cortex. Nectin molecules expressed in the Cajal-Retzius cell (Nectin1) and the migrating neuron (Nectin3) are also necessary for somal translocation. The initiation of detachment is signaled by SC1, which is expressed on the surface at the top and bottom of RGCs surfaces. The anti-adhesive signal is crucial to proper cortical development, as the absence of SC1 results in failure of neurons to detach and properly position. Dab1 interacts with Cullin5 in the migrating cell to accumulate in the appropriate cortical layer. Termination of polarization upon reaching the appropriate location is met by the degradation of reelin receptors, N-cadherin and Dab1 by exocytosis and endocytosis. E2, Estradiol; IZ, intermediate zone; MAZ, multipolar cell accumulation zone; CP, cortical plate; RGC, Radial glial cell; ERα, estrogen receptor alpha; ERβ, estrogen receptor beta; BP, bipolar; MP, multipolar; SEP, slow exiting population; REP, rapidly exiting population; SFK, Src family kinases; PI3K, Phosphoinositide 3 kinase; SC1, SPARC-like1; VLDLR, very low-density lipoprotein receptor; ApoER2, apolipoprotein E receptor 2; Cux2, cut like homeobox 2; FoxG1, Forkhead Box G1; Dab1, Disabled-1; Tbr1, T-box brain 1; Lis-1, Lissencephaly-1; Crk, (p38/adaptor molecule crk); C3G, CRK SH3-binding GNRP; Rap1, Ras-like GTPase; Satb(1/2) Special At-rich sequence binding protein (1/2); Robo1, Roundabout Guidance Receptor 1; EphA4, Ephrin type-A receptor 4; NSCs, neural stem cells.