FIGURE 6.
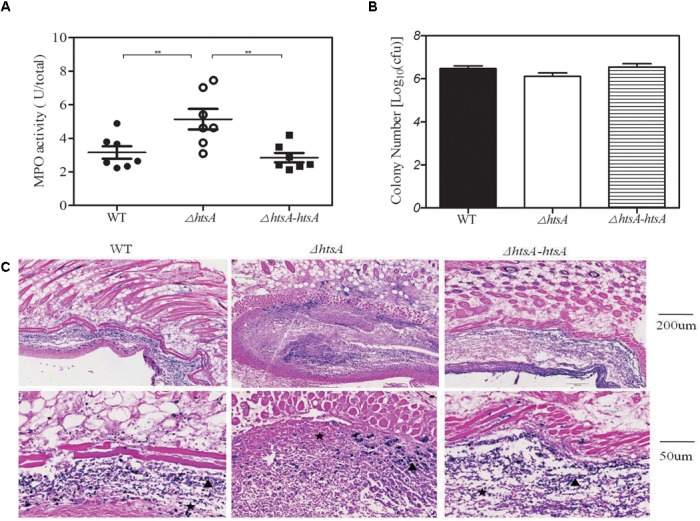
Deletion of htsA induced higher neutrophil recruitment at skin infection sites of mice. Groups of mice were subcutaneously injected with wild type, ΔhtsA, or ΔhtsA-htsA strains at a dose of ∼2.0 × 108 CFU, and the skin containing the infection area was excised and homogenized at 24 h postinfection. (A) MPO activity at skin infection sites of mice. The MPO activity (U/total) of mice infected with ΔhtsA was higher than that of mice infected with wild type or ΔhtsA-htsA. (B) The total bacterial CFU at skin infection sites of mice. There were no statistically significant differences in total bacterial CFU among the three GAS strains. (C) Microscopic pictures of Gram staining at a skin infection site.  inflammatory cells,
inflammatory cells,  bacteria. ∗∗P < 0.01.
bacteria. ∗∗P < 0.01.
