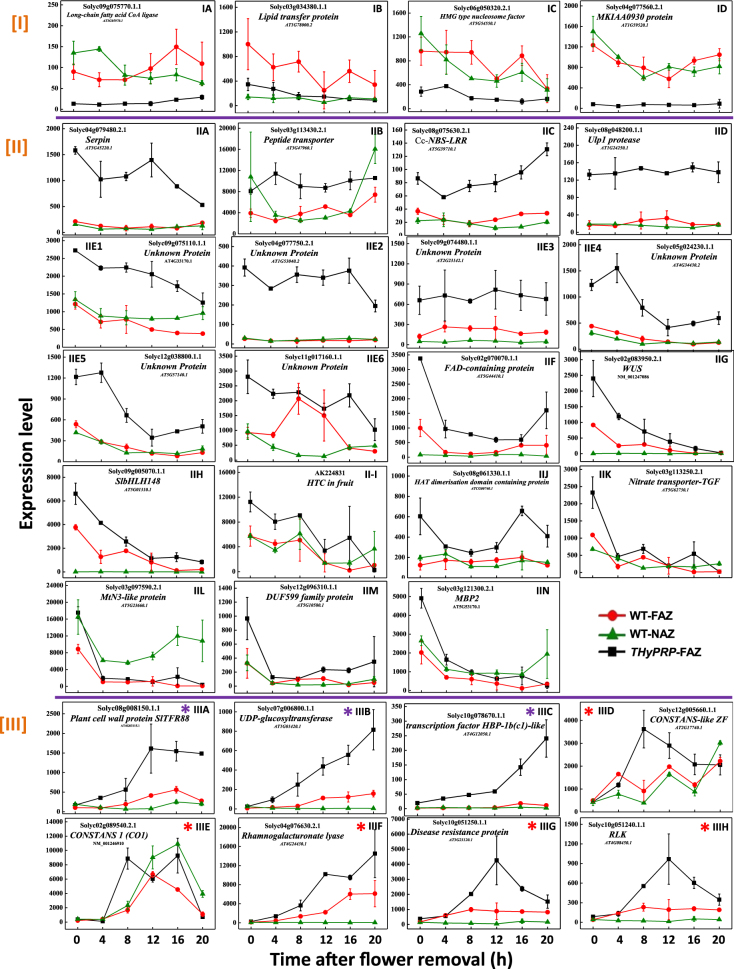
Fig. 5. Line graphs showing the kinetics of changes in array-measured expression levels of genes that were specifically and continuously downregulated [I] or upregulated [II] at zero time and later on, or upregulated at 4 (blue*) or 8 (red*) h after flower removal [III] in the FAZ of THyPRP-silenced plants.
TAPG4::antisense THyPRP-silenced line 11/generation T4 was used. Expression levels were measured for tomato Long-chain fatty acyl-CoA synthetase (IA); Lipid transfer protein (IB); High Mobility Group (HMG) type nucleosome factor (IC); MKIAA0930 (ID); Serine protease inhibitor (Serpin) (IIA); Peptide transporter (IIB); Nucleotide Binding Site—Leucine-Rich Repeat (Cc-NBS-LRR) (IIC); Ubiquitin-like protein1 (Ulp1 protease) (IID); unknown proteins (IIE1–E6); FAD-binding domain-containing protein (IIF); WUSCHEL-related homeobox-containing protein4 (WUS) (IIG); SlbHLH transcription factor148 (IIH); HTC in fruit (II–I); HAT dimerization domain-containing protein (IIJ); Nitrate transporter-TGF (IIK); MtN3-like protein (IIL); DUF599 family protein (IIM); Myrosinase-Binding protein2 (MBP2) (IIN); Plant cell wall protein SlTFR88 (IIIA); Uridine 5′-diphospho (UDP)-glucuronosyltransferase (IIIB); Transcription factor HBP-1b(c1)-like (IIIC); CONSTANS-like ZF (IIID); CONSTANS1 (CO1) TF (IIIE); Rhamnogalacturonate endolyase (IIIF); Disease resistance protein (IIIG); and defense-related Receptor-Like protein Kinase (RLK) (IIIH). Transcript identities are indicated in the graphs by their gene ID and their Arabidopsis (At) gene number and/or their nucleotide accession number. The results are means of two independent biological replicates ± SD