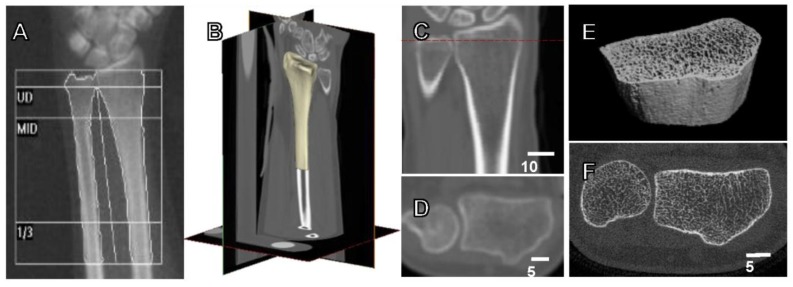
Figure 1.
Current available methods for the assessment of bone strength and fracture risk. (A) Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) forearm scan with standard ultradistal (UD), middle (MID) and one-third of arm length (1/3) regions, used to calculate aBMD (g/cm2). (B) 3D view of clinical computed tomography (CT) scan of the distal radius, with (C) coronal view containing dotted line indicating position of (D) transverse view. CT scan acquired at a transverse pixel size of 234 μm and slice thickness of 625 μm. (E) 3D view of high resolution peripheral quantitative CT (HRpQCT) image (F) of the distal radius, with isotropic voxel size of 82 μm.