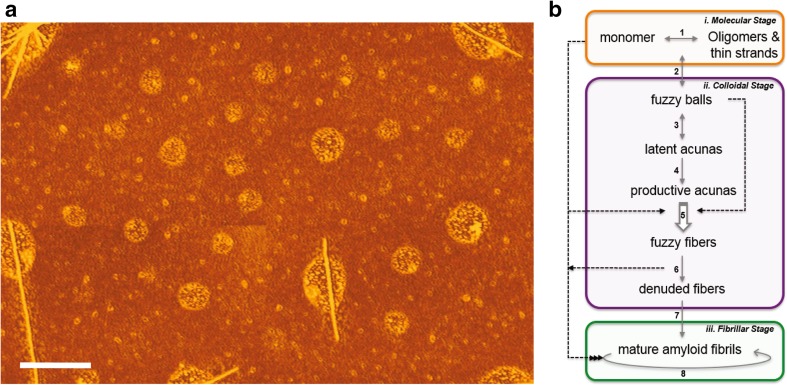
Fig. 1.
a AFM image of a field containing a variety of co-existing AS colloidal oligomers, intermediates, supramolecular structures and fuzzy deposited over a layer of monomeric and oligomeric AS. b Sequential aggregation scheme (SAS) for α-synuclein, summarized and adapted from (Fauerbach et al. 2012). The scheme depicts molecular, colloidal, and fibrillar stages for AS species in terms of the distinct reaction steps (numbered). (1) oligomerization (monomeric AS in equilibrium with e.g. dimers, tetramers). (2) Colloidal condensation (fuzzy and ball). (3) Supramolecular acunas. (4) Fibril elongation via activated productive acunas. (5) Generation and release of fuzzy fibers (the open arrow indicates a template function of the productive acunas). (6) Loss of fuzziness (denuded fibers) and transformation to other prefibrillar structures. (7) Conformational transition to the amyloid fibrillar form. (8) Fibrillar growth by mechanical fragmentation and terminal extension via scavenging of monomers and oligomers