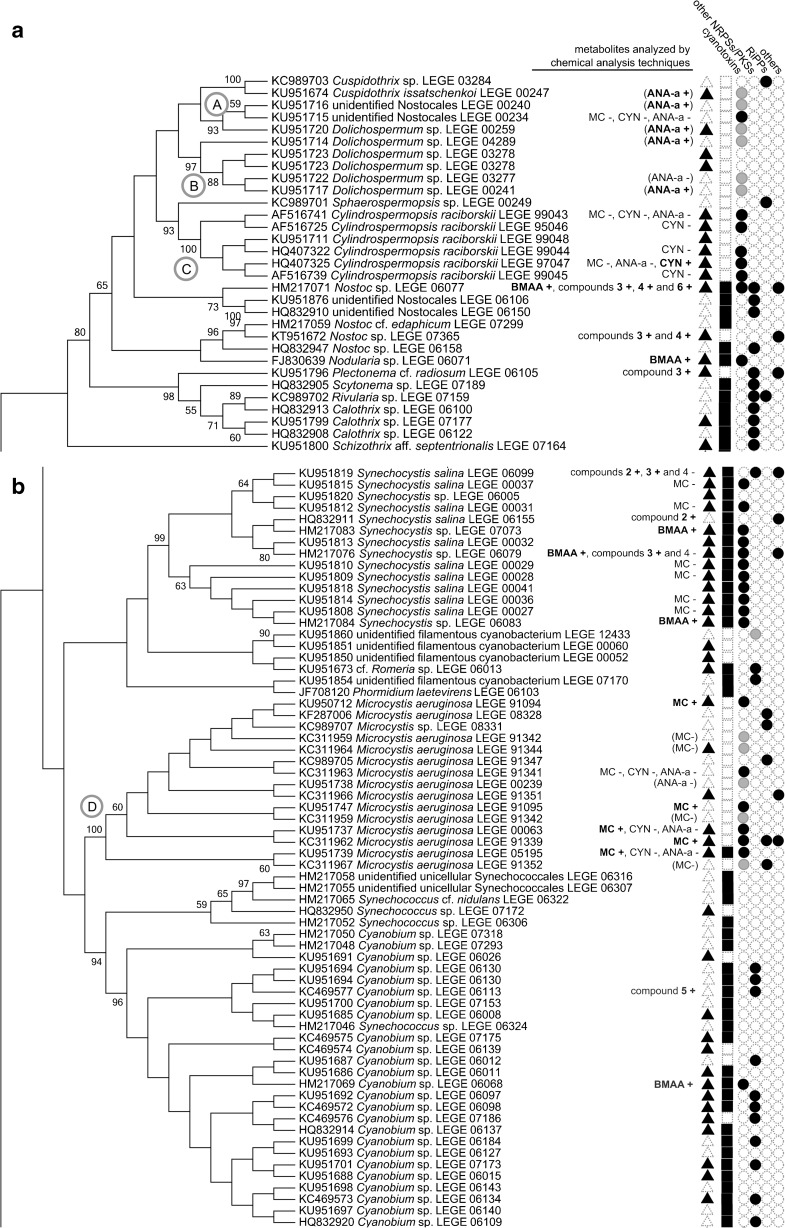
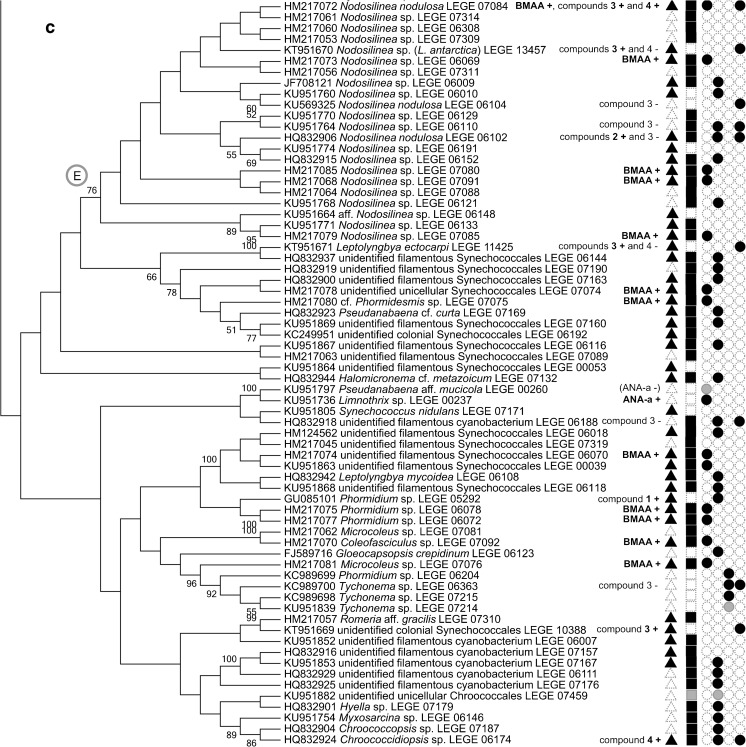
Fig. 4.
ML cladogram (− lnl = 3431.5512) for 165 LEGE CC strains having available data related to natural products. Capital letters in the tree highlight clades encompassing close-related strains for which the production of some of the following specific metabolites were detected (+) or not (−): Cyanotoxins: ANA-a anatoxin-a, BMAA β-Methylamino-L-alanine, CYN cylindrospermopsin, and MC microcystin. Bioactive compounds: 1 portoamides, 2 bartolosides, 3 dehydroabietic acid, 4 abietic acid, 5 hierridin B, and 6 anabaenopeptins A and D. Notice that the production (+) or absence of production (−) of the different compounds were confirmed by analytical techniques such as HPLC, LC-MS, or NMR. Metabolites between parentheses and symbols in gray indicate unpublished data. Symbols indicate the existence of data (either for the detection or non-detection) on: toxicity, bioactivity, or allelopathy assays (▲); screening of metabolites by MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry or by LC–MS analysis coupled with molecular networking [13] (■); cyanotoxins (•, first column); other than cyanotoxins nonribosomal peptide synthetases, polyketide synthases, or hybrid NRPS-PKS (•, second column); ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides (Martins et al. 2013) (•, third column); and other family of compounds such as terpenes, glycolipids, etc. (•, fourth column). To get at the data on a particular strain, please find the literature references in the corresponding catalog sheet (Online Resource 3)