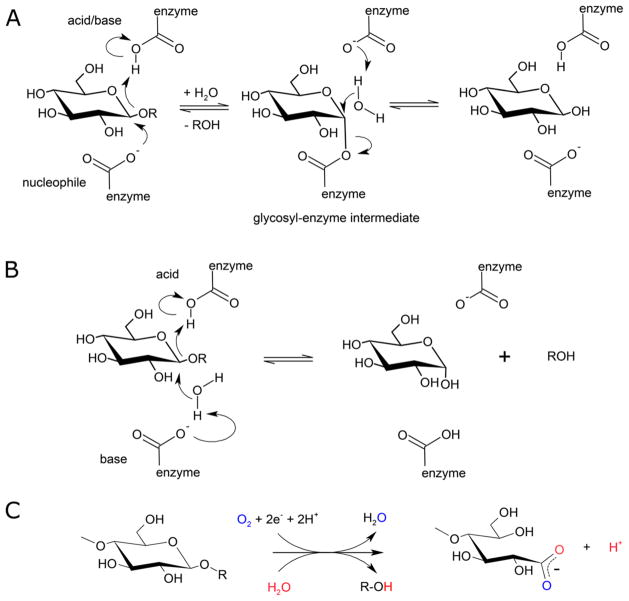
Figure 1.
Catalytic schemes for hydrolytic and oxidative cleavage of glycosidic bonds. (A) Retaining mechanism for hydrolysis of glycosidic bonds by glycoside hydrolases. (B) Inverting mechanism for hydrolysis of glycosidic bonds by glycoside hydrolases (Modified with permission from ref 2. Copyright 1995 Elsevier). (C) General scheme for oxygen and electron-dependent cleavage of glycosidic bonds by LPMOs. Vaaje-Kolstad et al. demonstrated that oxygen atoms from molecular oxygen and solvent water end up in reaction products.3 Ascorbic acid has been used extensively as an electron donor for LPMOs, but various other compounds and enzyme systems can provide electrons as well.4–6