Figure 17.
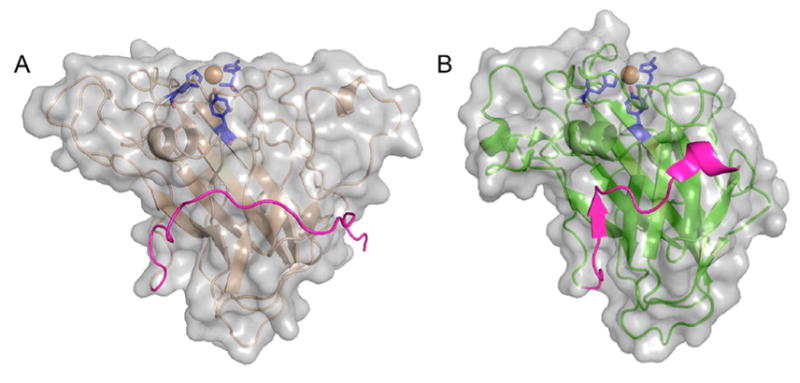
Extended C-terminal linker in T. reesei (H. jeocorina) LPMO9A and the extra residues in L. similis LPMO9A. Surface and cartoon representations of (A) HjLPMO9A (PDB ID 5O2X) and (B) LsLPMO9A (PDB ID 5ACJ).180 HjLPMO9A, active on crystalline substrates, has a flat surface, while Ls(AA9)A, active on both cellulose and soluble substrates, has a less pronounced binding surface also containing a “ridge-like” topology. Orientations of the two molecules are the same with the binding surfaces on top of the molecules. Catalytic sites with two histidines: one tyrosine (blue) and the copper atom (orange) are shown with sticks/sphere. Both structure models contain 15–20 extra C-terminal residues (magenta). While the native full-length HjLPMO9A has a CBM1 module, the native LsLPMO9A does not (see section 4.2).
