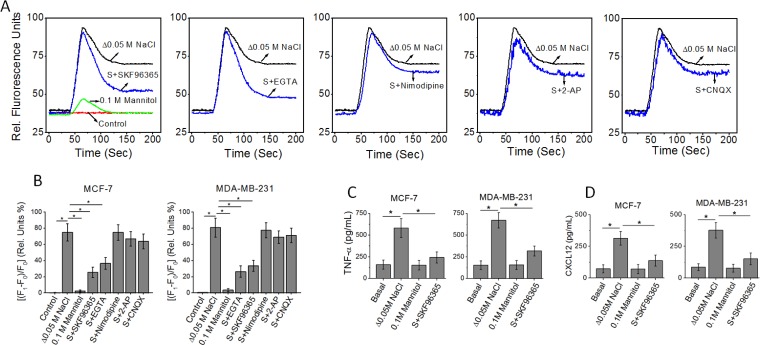
Figure 1.
(A) Fluo-3 Ca2+ measurement indicates that SKF96365 (10 μM, inhibitor of store operated Ca2+ entry) and EGTA (2 mM) treatments decrease high salt (Δ0.05 M NaCl) induced Ca2+ influx in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. The basal (normal salt) treatment is indicated in red as control. While inhibitors of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels (nimodipine, 10 μM), NMDA receptors (2-AP, 10 μM), or AMPA receptors (CNQX, 10 μM) had no effect on high salt-induced calcium influx. (B) Quantitative changes high salt induced calcium influx measured by relative florescence shift (ΔF/F*100) in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells following various treatment conditions. F1, plateau phase fluorescence; F0, baseline fluorescence. (C, D) Inhibition of inflammatory cytokine TNF-α (C), and inflammatory chemokine CXCL12 (D) expression MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells in following treatment with SOCE inhibitor. Data were representative of five experiments and shown as mean ± SEM, p < 0.05.