Figure 11.
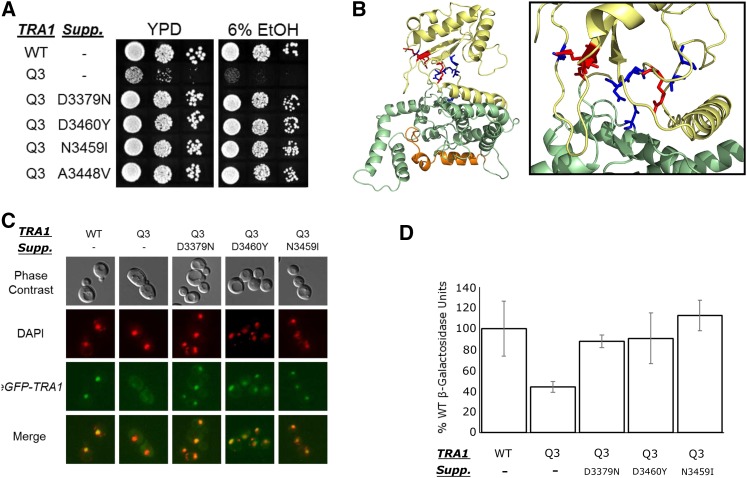
Second site suppressors of tra1. (A) Second site suppressors rescue slow growth of tra1. Yeast strains CY4353 (TRA1), CY6582 (tra1) and four independent suppressors that restore growth of tra1 on media containing ethanol were grown to stationary phase in media lacking leucine to maintain YCplac111-YHR100C, diluted in 10-fold dilutions and spotted onto YPD or YPD containing 6% ethanol and grown at 30° for two days. (B) Intragenic suppressors were mapped onto the cryo-EM Tra1 structure (Diaz-Santin et al. 2017). The three initial arginine to glutamine mutations are highlighted in red. Residues that suppressed tra1 are blue. (C) Second site suppressors restore nuclear localization of Tra1. An N-terminal eGFP tag was integrated in front of four tra1 suppressor alleles. Yeast strains CY5998 (eGFP-TRA1), CY7341 (eGFP-tra1) and the GFP tagged suppressors were grown to stationary phase in media lacking uracil, diluted 1:20 and grown to mid-logarithmic phase and stained with DAPI. Cells were washed twice with water before imaging. (D) Second site suppressors restore transcription defects of tra1. Strains BY4741 (TRA1), CY6635 (tra1) and suppressor strains CY6909 (tra1-D3379N), CY6902 (tra1-D3460Y), and CY6940 (tra1-N3459I) were transformed with SRE-lacZ on a LEU2 centromeric plasmid. Strains were grown to saturation in media lacking leucine before being diluted 1:10 in YPD with 6% ethanol grown for eight hours. β-galactosidase activity units are the average of three replicates with the SD shown by the error bars.