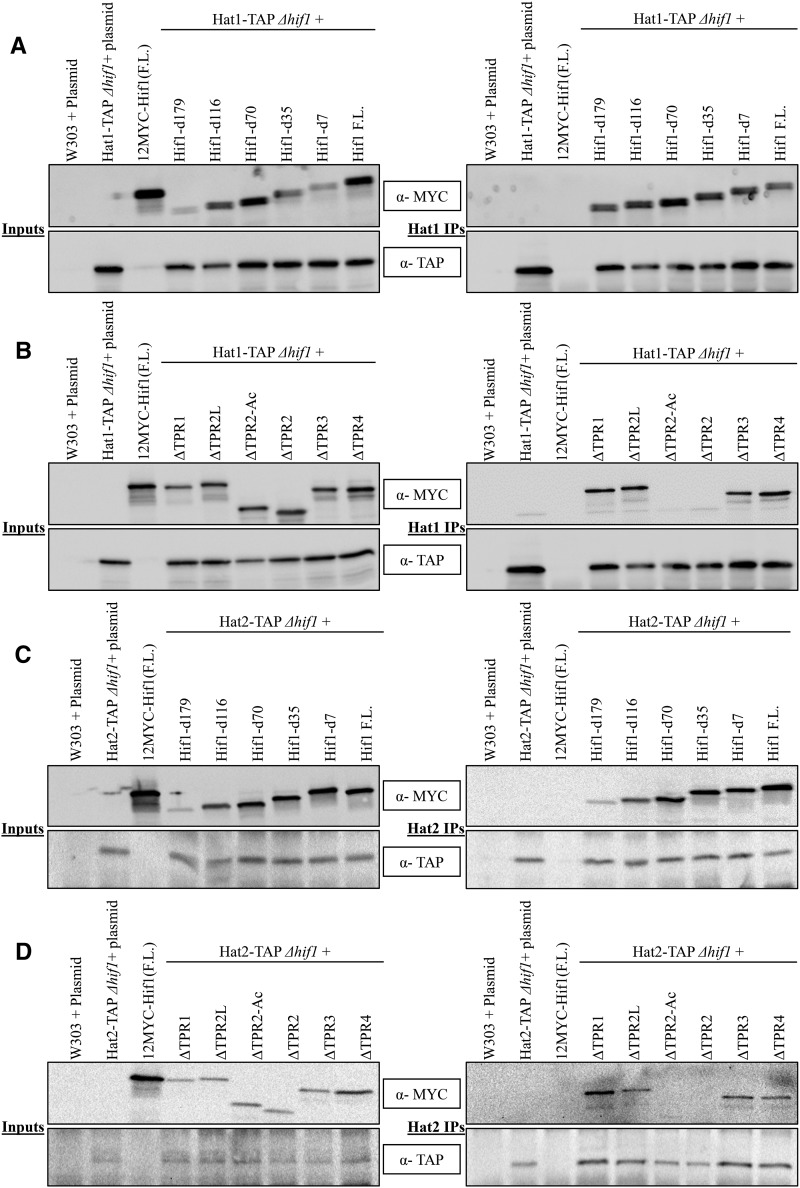
Figure 2.
Western blot analysis of Co-IP fractions of Hat1/2-TAP and Hif1 C-terminal (external) and internal deletions constructs. A: (Left) Input fractions of Co-IP experiments for various Hif1 C-terminal (external) deletions. (Right) Western blot analysis of Co-IP fractions of Hif1 C-terminal mutants to assess their ability to immunoprecipitate with Hat1-TAP B: (Left) Input fractions of Co-IP experiments for various Hif1 internal deletion mutants. (Right) Co-IP samples of Hif1 internal deletions. C: (Left) Input fractions of Co-IP experiments for various Hif1 C-terminal (external) deletions. (Right) Western blot analysis of Co-IP fractions of Hif1 C-terminal mutants to assess their ability to immunoprecipitate with Hat2-TAP D: (Left) Input fractions of Co-IP experiments for various Hif1 internal deletion mutants. (Right) Co-IP samples of Hif1 internal deletions. The red arrows represent the position of HAT2. Note: The size difference of various Hif1 truncated mutants represents various deletions. The top panels were probed with anti-MYC antibody whereas bottom panels were probed with anti-TAP antibody.