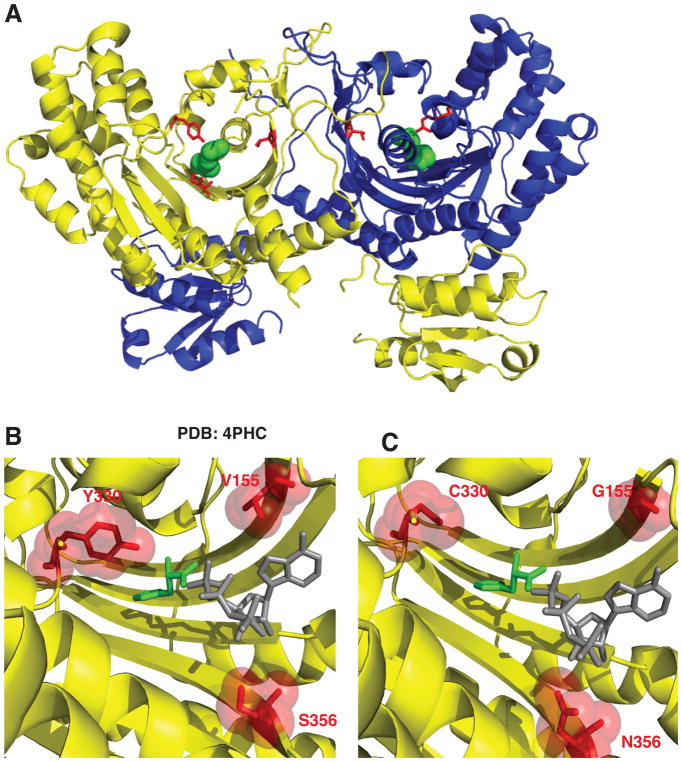
Figure 2. Histidyl-tRNA synthetase CMT variants are found in the active site of the dimeric enzyme.
(A) Histidyl-tRNA synthetase forms a homodimer (first monomer yellow and second monomer blue). The neuropathy-associated HARS residues are shown in the 3D structure as red sticks of the HARS dimer bound to histidine (green spheres) (PDB 4PHC). (B) The HARS active site pocket (yellow) reveals that neuropathy-associated mutations face into the active site (shown as red sticks and spheres). (C) Modeling in HARS neuropathy-associated substitutions indicates that interference with substrate binding (histidine green sticks and ATP gray sticks) can occur. ATP was modeled into the active site of the human HisRS bound to histidine (PDB 4PHC) by aligning the HisRS E. coli structure bound to ATP (PDB 1KMN).