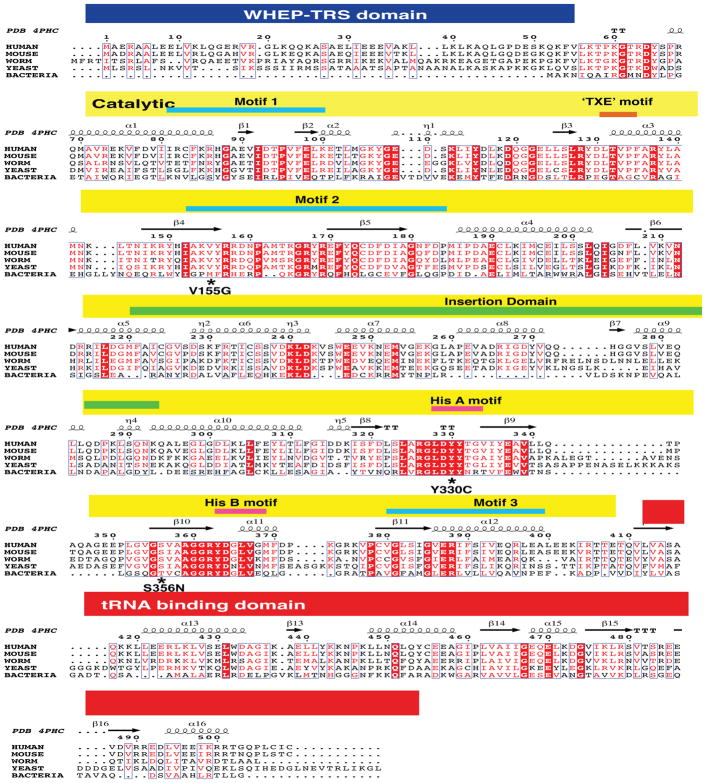
Figure 3. Neuropathy-associated HARS mutations are highly conserved.
(A) Multiple-species protein alignments were generated to assess the conservation of each affected amino-acid position. Complete amino acid sequence alignment of human, mouse, worm, yeast, and bacterial HARS were generated with Clustal Omega and annotated with quaternary structural information with ENDscript (Robert and Gouet, 2014). The position of known functional domains of the HARS protein indicated in blue (WHEP-TRS domain of unknown function), red (catalytic core), and yellow (tRNA binding domain) and motifs critical for substrate binding are indicated along the top. For each of the three variants, the affected amino acid is indicated by an * in the HARS protein sequence in multiple, evolutionarily diverse species. Note that strictly conserved residues are highlighted in red with white lettering while slightly conserved residues across multiple but not all species are red.