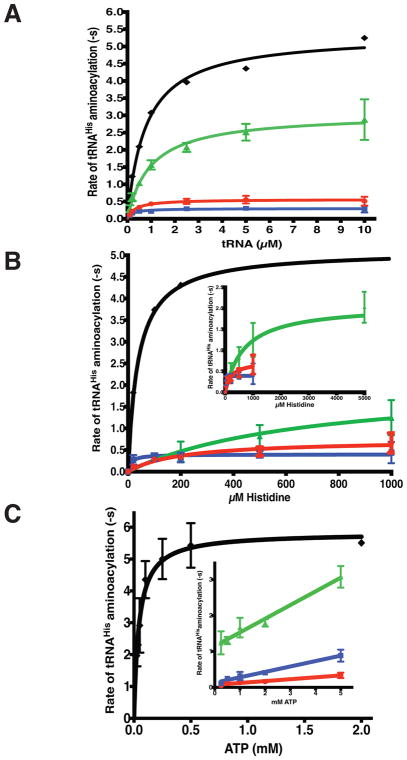
Figure 6. Identification of specific catalytic defects in neuropathy associated HARS CMT mutants by steady state kinetics.
Multiple turnover aminoacylation reactions were performed under Michaelis-Menten conditions of excess substrates and limiting enzyme as described in “Materials and Methods.” Initial velocity of product formation was plotted against substrate concentration for A, tRNA; B, Histidine, and C, ATP. Fits to the Michaelis-Menten equation returned kcat and KM values, which are reported in Table 2. The plots are color coded as in Figure 5: wild-type HARS (black diamonds, ◆); p.Val155Gly HARS (green triangles, ▲); p.Tyr330Cys HARS (red circles, ●), and p.Ser356Asn HARS (blue squares, ■). When ATP was the variable substrate, none of the mutants reached a saturating velocity at the highest ATP concentration (5 mM). The inset shows linear fits of the V/S data for the mutants to allow an estimation of kcat/KM. Each point represents the mean of three independent experiments, and error bars indicate the standard error.