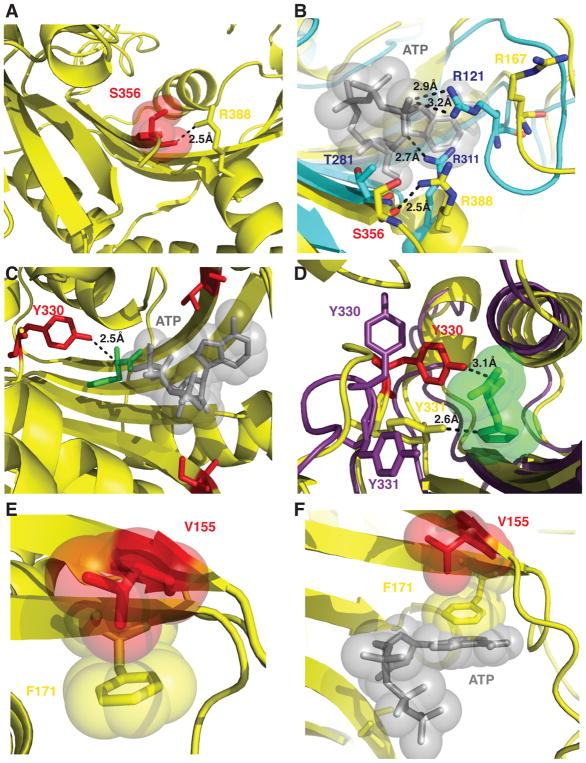
Figure 8. Molecular interactions of HARS neuropathy-associated amino acid residues in the active site.
(A) S356 is positioned in the active site to coordinate a critical arginine residue R388 in motif 3. (B) R388 is highly conserved and corresponds to R311 in E. coli HisRS structure (cyan) that is responsible for positioning the γ phosphate of ATP adjacent R121. (C) Y330 is situated 2.5 Å from the alpha carbon of histidine (green) but makes no immediate interactions with modeled ATP (gray sticks and spheres). (D) Y330 and Y331 facilitate hydrogen bonding interactions with histidine. Y330 in the apo enzyme (shown as purple sticks) can flip away from the active site and swing 8 Å upon histidine binding (shown as red sticks) to facilitate hydrogen bonding interactions. (E) Phe 171 forms a stacking interaction with the ribose ring of ATP (as modeled in the active site as grey sticks and spheres). (F) p.Val155Gly is buried in the active site and does not mediate any direct interactions with either substrate histidine or ATP, but in the apo enzyme forms a CH-Pi interaction with the aromatic ring of Phe 171 within the active site.