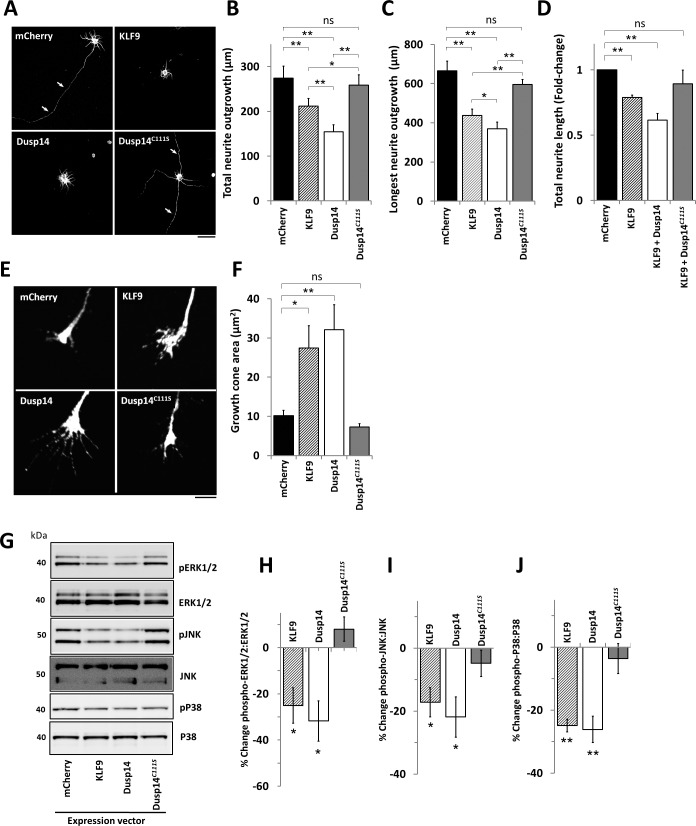
Figure 3.
Dusp14 activity is required for Dusp14- and KLF9-induced RGC axon growth inhibition and MAPK dephosphorylation. (A–D) Neurite growth was inhibited by Dusp14 and KLF9 but not Dusp14C111S. Neurite growth of RGCs co-transfected with KLF9 and Dusp14 or Dusp14C111S (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, paired t-test). (E) Morphology of the growth cones of RGCs transfected with KLF9, Dusp14, and Dusp14C111S. (F) RGCs transfected with KLF9 and Dusp14 led to enlarged growth cones, whereas Dusp14C111S showed growth cones morphology similar with mCherry control. (G) Western blots for total ERK1/2, phospho- (p-) ERK1/2, total JNK, p-JNK, total P38 and p-P38 were analyzed in RGCs after gene transduction. (H–J) Densitometry of p-MAPK/total MAPK ratios: in Dusp14-transduced RGCs, the phosphorylation ratio of ERK1/2 (H), JNK (I), and P38 (J) were decreased 31.8%, 21.9%, and 26.1%, respectively. KLF9 induced a similar reduction of phosphorylation, but Dusp14C111S showed no effect. (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. control, paired t-test, n = 4; WT, wildtype). Scale bar: 5 μm in (A), 50 μm in (E). Error bars: SEM.