Figure 3. NMDA‐induced increase in interaction with GW182 is caused by Ago2 phosphorylation at S387.
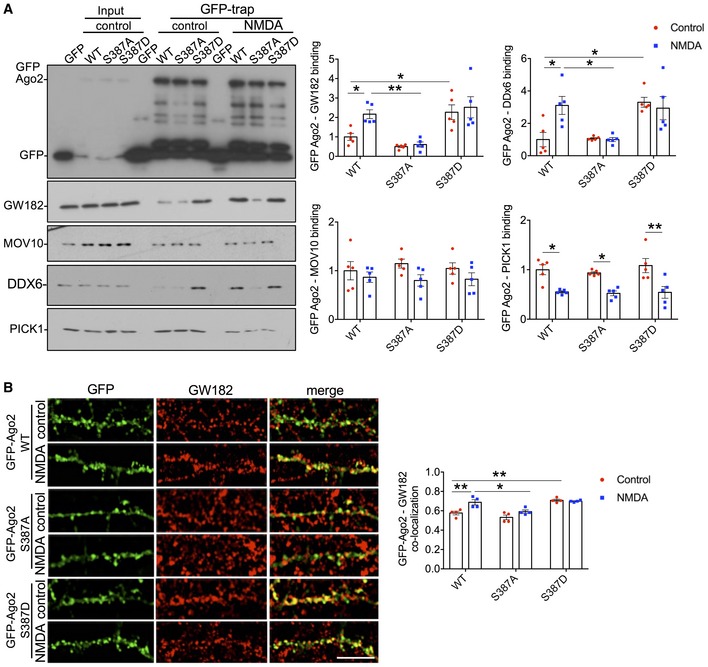
- Ago2 S387A mutation blocks, and S387D mutation occludes NMDA‐induced increases in GW182 and DDX6 interactions. Cortical neurons were transfected with molecular replacement constructs expressing Ago2 shRNA plus shRNA‐resistant GFP‐Ago2 (WT, S387A or S387D). Lysates were prepared 10 min after NMDA washout, and GFP‐Ago2 complexes were precipitated using GFP‐trap beads. Bound proteins were detected by Western blotting using GFP, GW182, MOV10, DDX6 or PICK1 antibodies as shown. Graphs show quantification of GFP‐Ago2 interactions, normalised to untreated WT condition; n = 5. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; two‐way ANOVA, Bonferroni post hoc test. Mean ± SEM.
- Ago2 S387A mutation blocks, and S387D mutation occludes NMDA‐induced increase in GW182 co‐localisation in neuronal dendrites. Cortical neurons were transfected with molecular replacement constructs expressing Ago2 shRNA plus shRNA‐resistant GFP‐Ago2 (WT, S387A or S387D), fixed 10 min after NMDA washout, permeabilised and stained with GW182 and GFP antibodies. Graph shows Pearson's co‐localisation coefficients; n = 4 independent experiments (11 cells per condition). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; two‐way ANOVA, Bonferroni post hoc test. Scale bar = 10 μm. Mean ± SEM.
Source data are available online for this figure.
