Figure 1.
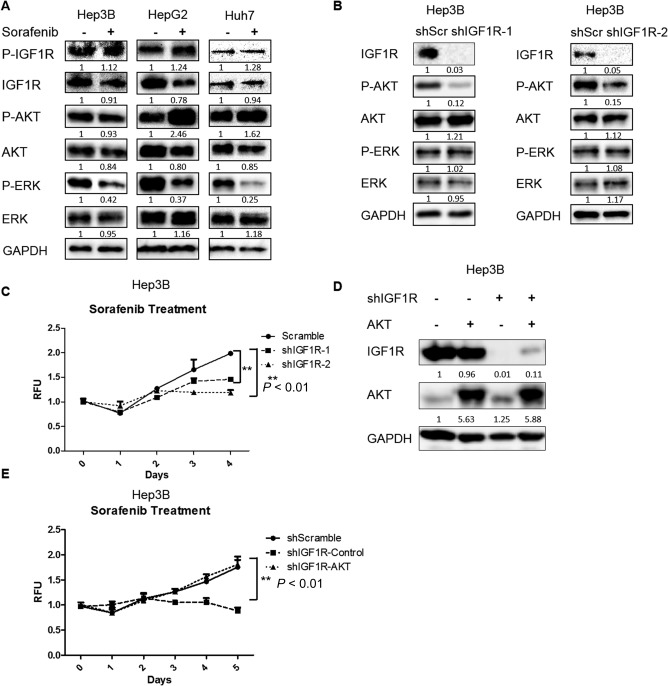
Knockdown of IGF1R enhanced the inhibitory efficacy of sorafenib in HCC cells by inhibiting AKT. (A) HCC cells were treated with sorafenib (1.25 μM for Hep3B, 2.5 μM for HepG2, and 5 μM for Huh7) for 24 hours. Expressions of p‐IGF1R, IGF1R, p‐AKT (ser473), AKT, p‐ERK, ERK, and GAPDH proteins were examined by western blotting. (B) Expressions of IGF1R, p‐AKT (ser473), AKT, p‐ERK, ERK, and GAPDH proteins were examined by western blotting in Hep3B cells infected with IGF1R shRNAs and scrambled shRNA lentiviral particles. (C) Cell proliferation was analyzed by the alamarBlue assay in Hep3B cells infected with IGF1R shRNAs and scrambled shRNA lentiviral particles and then treated with 1.25 μM sorafenib. (D) Expressions of IGF1R, AKT, and GAPDH proteins were examined by western blotting in Hep3B cells infected with scrambled shRNA, IGF1R shRNA, constitutively active AKT, or both lentiviral particles. (E) Cell proliferation was analyzed by the alamarBlue assay in IGF1R knockdown Hep3B cells infected with control or constitutively active AKT lentiviral particles and then treated with 1.25 μM sorafenib. Each experiment was repeated at least 3 times. Abbreviations: GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3‐phosphate dehydrogenase; RFU, relative fluorescence unit; shScr, short hairpin scrambled. Values in C and E were mean ± SD (n = 3 in each group).
