Figure 7.
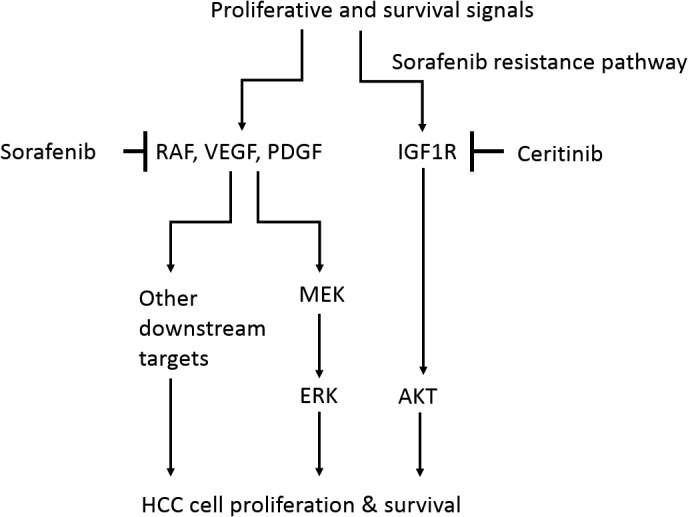
Schematic model. Sorafenib inhibits its downstream targets RAF, VEGF, and PDGF, resulting in inhibition of MEK/ERK activity, which leads to inhibition of HCC cell proliferation and survival. However, HCC cells are able to escape from sorafenib's effects using other resistance pathways that sorafenib insufficiently inhibits. IGF1R/AKT is such a sorafenib‐resistant pathway. IGF1R remains activated after sorafenib treatment in HCC cells and its activity leads to AKT activation, which is critical for HCC cell proliferation and survival. Ceritinib is a potent IGF1R inhibitor. Ceritinib effectively inhibits the IGF1R/AKT pathway but fails to suppress ERK activity. Therefore, ceritinib alone has a modest effect on HCC cell proliferation and survival. The combination of sorafenib and ceritinib effectively inhibits both the MEK/ERK and IGF1R/AKT pathways, which results in more effective inhibition of HCC cell growth compared to either sorafenib or ceritinib used alone. Abbreviations: MEK, mitogen‐activated protein kinase/ERK kinase; PDGF, platelet‐derived growth factor.
