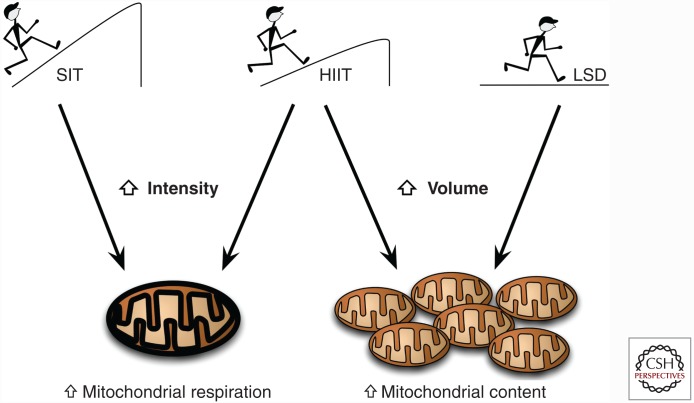
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of training intensity and volume on mitochondrial respiration versus content adaptations through endurance training. Recent evidence suggests that increases in exercise intensity (sprint interval training [SIT]; high-intensity interval training [HIIT]) lead to enhanced mitochondrial respiration and function, whereas prolonged low-intensity and high-volume (long slow-distance [LSD] training) endurance exercise appears to aid in increased mitochondrial content within skeletal muscle.