Figure 1. Method of colocalisation analysis.
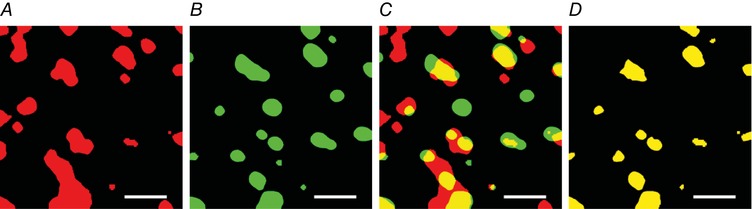
Binary images of objects representing HSL (A) and LDs (B) identified by a selected intensity threshold to signify a positive signal for HSL or LDs, respectively. C, colocalisation of HSL objects and LDs was investigated by merging the images. D, the extracted objects represent positive colocalisation between HSL and LDs. Any LD that overlapped with a HSL object was counted as a colocalisation event. If the same HSL object overlapped more than once with a LD then this was counted as a dual colocalisation event and omitted from the analysis, allowing for only one colocalisation event to be counted. The same procedure was used to obtain colocalisation analysis for ATGL objects and LDs, and PLIN2 or PLIN5 and LDs. Scale bars represent 3 μm. [Color figure can be viewed at http://wileyonlinelibrary.com]
