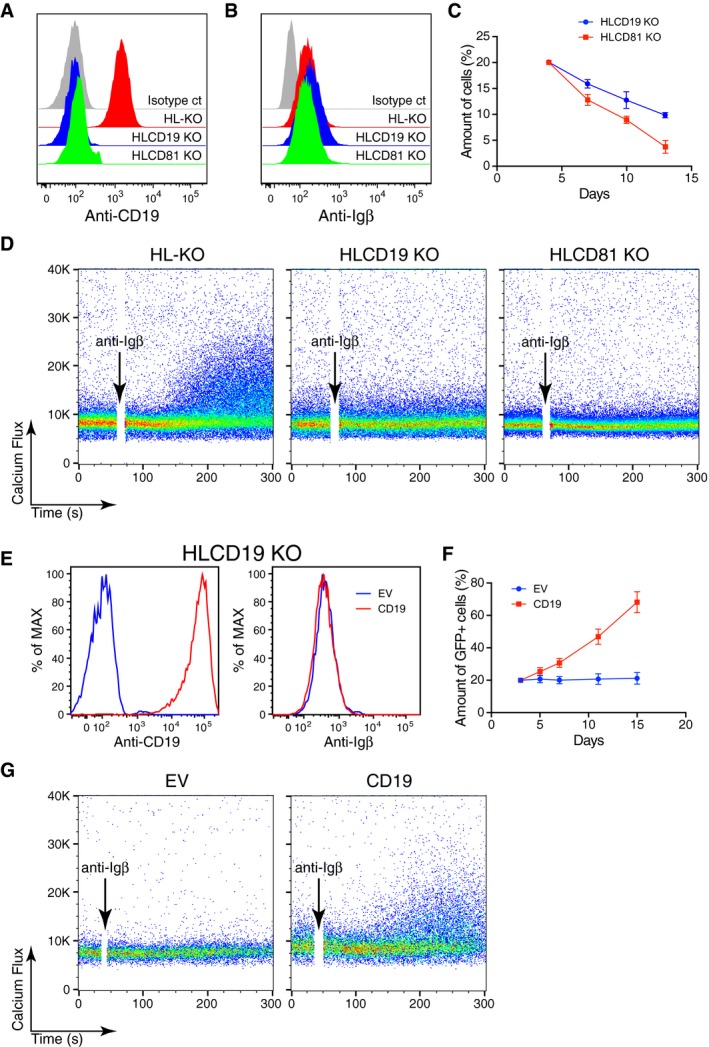
Figure 5. The Igβ‐dependent Ramos cell fitness requires CD19.
-
A, BThe expression of CD19 and Igβ on the surface of different Ramos KO cells was determined by flow cytometry.
-
CThe CD19 and CD81 genes in HL‐KO Ramos cells were rendered defective by the CRISPR/Cas9 method, and the percentage of the CD19‐ or CD81‐negative cells in the triple KO population was measured by flow cytometry at the indicated time points. The data represent the mean and standard error of three independent experiments.
-
DCalcium responses of HL‐KO, HLCD19 KO, and HLCD81 KO cells stimulated by anti‐Igβ antibodies. The data are representative of three independent experiments.
-
EExpression of CD19 or Igβ on the surface of HLCD19 KO cells transduced with empty vector (EV) or the CD19 vector measured by flow cytometry.
-
FPercentage of GFP‐positive HLCD19KO cells at different time points after their transduction with EV or the CD19 expression vector. The data represent the mean and standard error of three independent experiments.
-
GCalcium responses of HLCD19 KO cells transduced with EV or CD19 expression vector after their stimulation with anti‐Igβ antibodies. The data are representative of three independent experiments. One clone is used for HL‐KO. HLCD19KO and HLCD81 KO are batch sorted.
