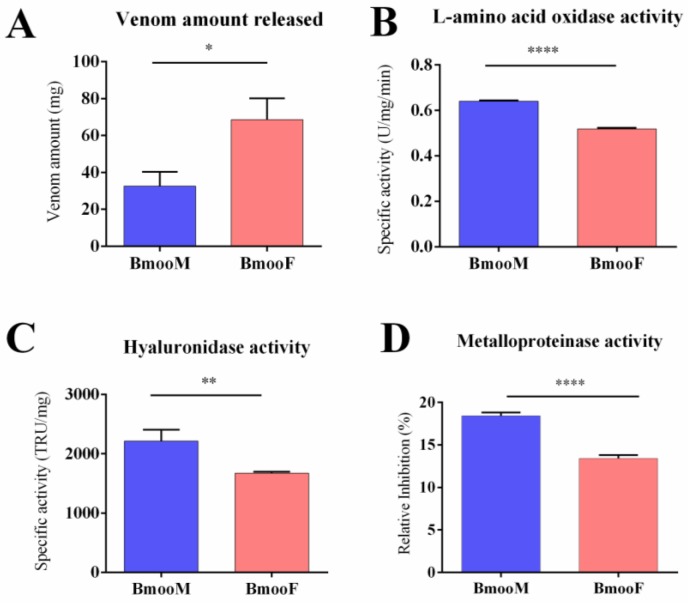
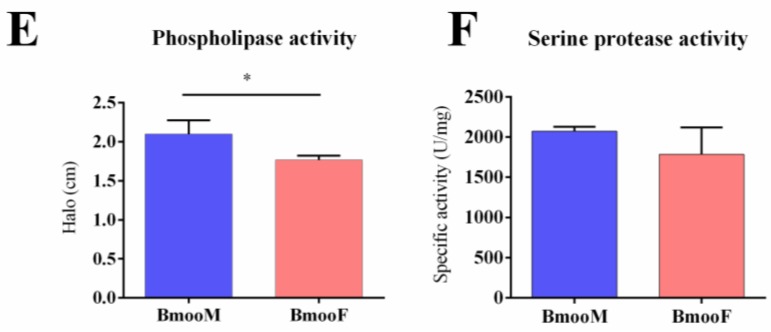
Figure 1.
Functional characterization of B. moojeni venom stratified by snake gender. BmooF = female snake; BmooM = male snake. (A) Amount of venom released during manual extractions; (B) L-amino acid oxidase specific activity determined using o-phenylenediamine as substrate; (C) Hyaluronidase specific activity determined by hydrolysis of hyaluronan, measured through a turbidimetric assay. TRU: turbidity-reducing units; (D) Metalloproteinase activity determined using the azocasein assay. Results are expressed as relative inhibition of the activity after venom incubation with ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA); (E) Phospholipase activity determined using egg-yolk agar plate medium. The size of the halos formed indicate the rate of phospholipase activity; (F) Serine protease specific activity determined using Nα-p-tosyl-L-arginine methyl ester (TAME) as substrate. The results are expressed as mean ± SD. Statistics (Student’s t test): (A) * p < 0.011; (B) **** p < 0.0001; (C) ** p < 0.0079; (D) **** p < 0.0001; (E) * p < 0.0341; and (F) p = 0.2145.