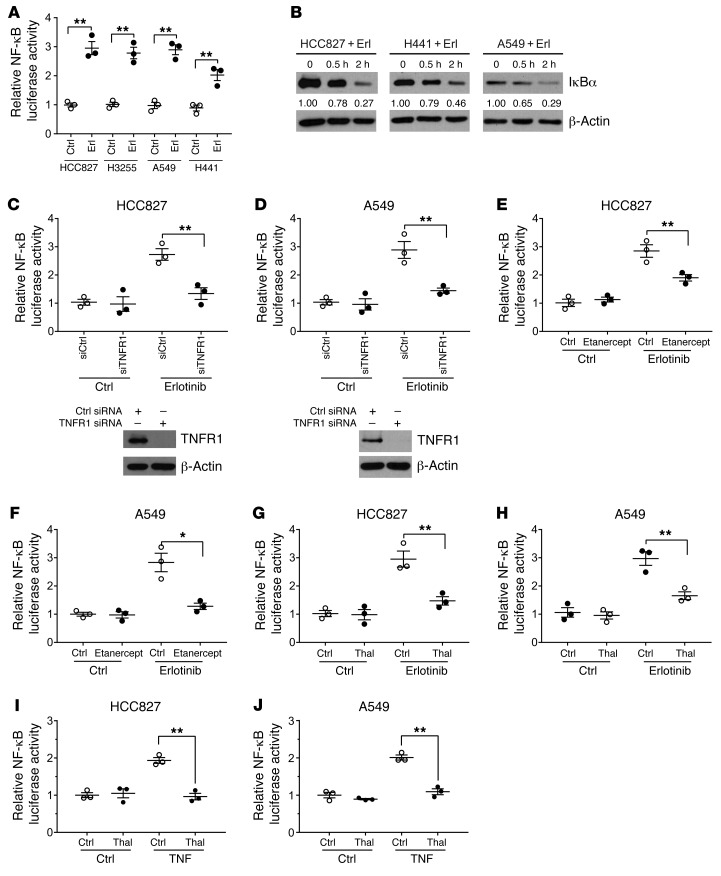
Figure 3. EGFR inhibition induces a TNF-dependent activation of NF-κB.
(A) HCC827, H3255, A549, and H441 cells were exposed to erlotinib (100 nM for EGFR-mutant and 1 μM for EGFRwt cells) for 24 hours followed by a dual luciferase reporter assay. Renilla luciferase was used as an internal control. (B) Cells were treated with erlotinib at various time points followed by preparation of cell lysates and Western blot with an IκBα antibody. Western blots are representative of at least 3 independent replicates. The quantified values reflect the ratios of IκBα/actin. (C) siRNA knockdown of TNFR1 was performed in HCC827 cells followed by transfection of cells with an NF-κB luciferase reporter and exposure of cells to erlotinib, followed by a reporter assay. Silencing of TNFR1 was confirmed with a Western blot. (D) A similar experiment was undertaken in A549 cells, and TNFR1 silencing was confirmed with a Western blot. Western blots shown in C and D are representative of at least 3 independent replicates. (E) The TNF-blocking drug etanercept was used at a concentration of 100 μg/ml along with erlotinib for 24 hours followed by a reporter assay in HCC827 cells. (F) A similar experiment was conducted in A549 cells. (G and H) Reporter assay for NF-κB in cells treated with erlotinib in the presence or absence of thalidomide (5 μg/ml) for 24 hours. (I and J) HCC827 and A549 cells were treated with exogenous TNF (10 ng/ml) with or without thalidomide for 24 hours followed by a reporter assay for NF-κB transcriptional activity. In luciferase assays, cells were transfected with reporter 24 hours before exposure to erlotinib. Data represent the mean ± SEM. n = 3 biologically independent experimental replicates (A and C–J). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, by Student’s t test. Erl, erlotinib; Thal, thalidomide.