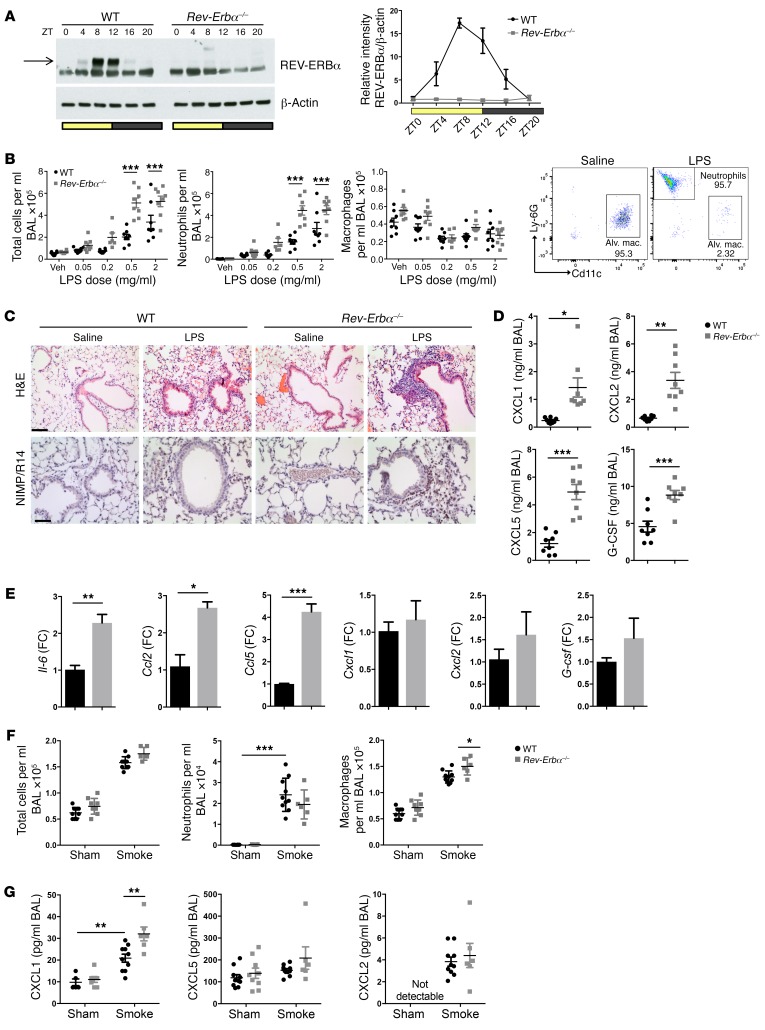
Figure 1. REV-ERBα plays a critical role in regulation of lung inflammation.
(A) Whole-lung REV-ERBα protein across the day (ZT, time from lights on). REV-ERBα densitometry (mean ± SEM) was normalized to β-actin and to WT at ZT0; n = 5 for WT and n = 3 for Rev-Erbα–/– per time point. (B) Mice were exposed to aerosolized LPS at ZT4 and culled 5 hours later; cellular infiltrates were quantified in BAL using flow cytometry. Data presented as mean ± SEM; n = 6–8, ***P < 0.001 (2-way ANOVA, post hoc Bonferroni). Veh, vehicle. (C) H&E staining and immunohistochemistry for the neutrophil maker (NIMP/R14) of lung sections from mice after LPS challenge at 2 mg/ml. Representative of n = 4; scale bars: 50 μm. (D) Cytokine/chemokine levels in BAL fluid from mice exposed to aerosolized LPS (2 mg/ml). Representative of n = 8, Student’s t test with Welch’s correction. (E) Quantitative PCR (qPCR) analysis of cytokine transcripts in alveolar macrophages isolated from mice and stimulated ex vivo with LPS at 100 ng/ml for 2 hours. Data normalized to WT and presented as mean ± SEM; n = 3, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (Student’s t test). FC, fold change. (F) Ten-day cigarette smoke exposures were performed between ZT8 and ZT10, and animals were culled 20 hours after the last exposure. Cellular infiltrates were quantified in BAL using a hemocytometer for total cell number and cytospin for neutrophil and macrophage counts. Data presented as mean ± SEM; n = 6–10, *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001 (2-way ANOVA, post hoc Bonferroni). (G) Chemokine levels in BAL fluid after 10-day cigarette smoke exposures. Data presented as mean ± SEM; n = 6–10, **P < 0.01 (2-way ANOVA, post hoc Bonferroni).