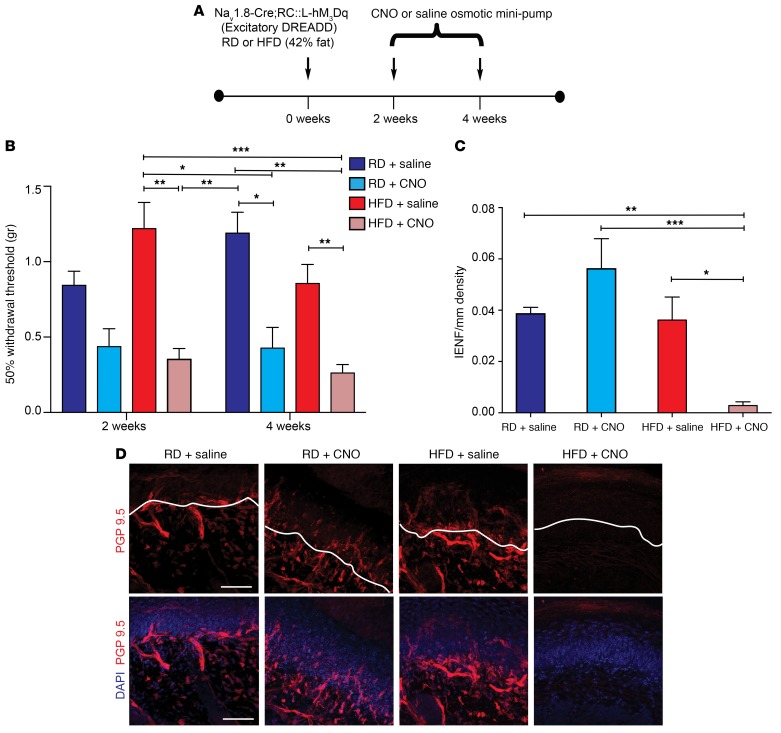
Figure 12. Long-term chemogenetic activation of Nav1.8-positive DRG neurons results in significant acceleration of the development of mechanical allodynia and small-fiber degeneration in HFD-fed mice.
(A) Experimental setup of osmotic mini-pump implantation in Nav1.8-Cre;RC::L-hM3Dq mice. Nav1.8-Cre;RC::L-hM3Dq mice that expressed excitatory hM3Dq DREADD receptors were fed either a RD or a HFD and underwent i.p. implantation of an osmotic mini-pump, which administered either saline or CNO (10 mg/kg/day) for the period from 2 to 4 weeks following the commencement of a HFD or RD. (B) von Frey pain behavior testing demonstrated the onset of mechanical allodynia (reduction in withdrawal threshold) in HFD-fed mice (red) after 2 or 4 weeks following CNO administration. The RD mice (blue) also showed a reduction of their withdrawal threshold after 4 weeks of CNO administration. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 (n = 6/group). (C and D) Quantification (C) and confocal micrographs (D) of skin from Nav1.8-Cre;RC::L-hM3Dq mice on a RD for 4 weeks with saline mini-pumps showed normal skin innervation using PGP 9.5 (pseudo-colored red). Sections were colabeled with the nuclear marker DAPI (blue). In contrast, HFD mice with CNO mini-pumps had significant depletion of nerve terminals. Interestingly, in RD mice, increased excitability alone, produced by hM3Dq DREADD receptors, was not able to induce small-fiber degeneration in the absence of diabetes. Scale bar: 50 μm. This effect was quantified in C using IENF density, and the epidermal-dermal junction is outlined in white in D. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 (n = 6 from each group, with 3 noncontiguous sections analyzed per sample). P values were calculated using a 1-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test. Values are expressed as the mean ± SEM.