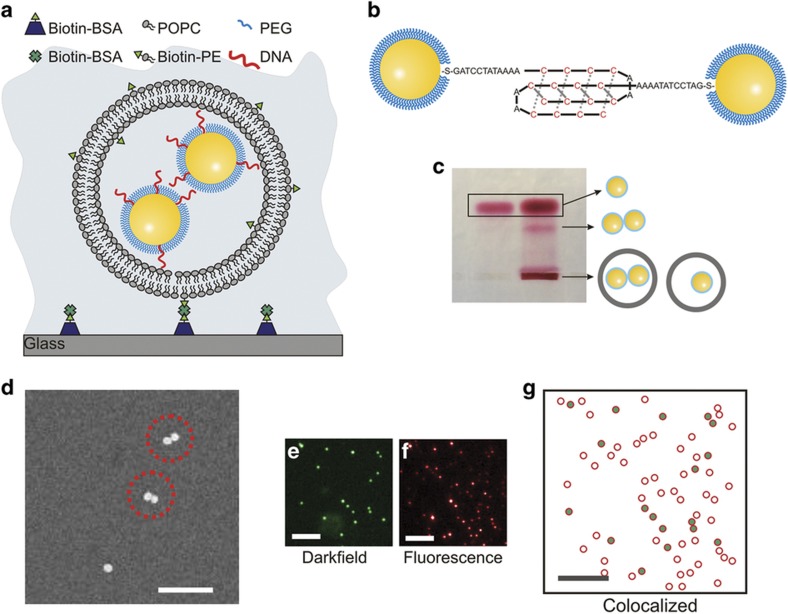
Figure 1.
Characterization of NP-liposomes. (a) Schematic drawing of liposome-encapsulated NPs (NP-liposome). (b) Model of DNA-NPs functionalized with DNA strands that are integrated into a self-assembled monolayer of short PEGs. The cytosine-rich single-stranded DNA strands facilitate the formation of bimolecular i-motif-like binding contacts between DNA-NPs under acidic buffer conditions. (c) Right lane: Electrophoresis of NP-liposome in 1% agarose gel. Left lane: DNA-NP controls that are not encapsulated in a liposome. Assignments of the bands are included as schematic drawings. (d) SEM pictures of NP-liposomes; scale bar, 350 nm. (e) Darkfield scattering image, (f) fluorescence image, and (g) magnified overlap image of a typical NP-liposome preparation after surface immobilization: the green dots mark the positions of the detected NPs; the red circles show the positions of the liposomes. The scale bars are 10 μm in (e–g). NP, nanoparticle; PEG, polyethylene glycol; SEM, scanning electron microscopy.