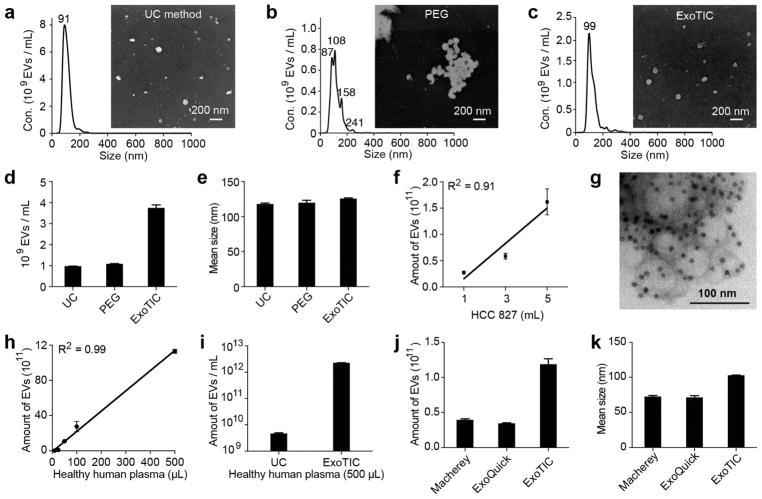
Figure 2.
Physical properties of EVs isolated by different methods. NTA and SEM analysis of EVs isolated by (a) UC, (b) PEG-based precipitation, and (c) ExoTIC. (d) Yield comparison of EVs purified from HCC827 lung adenocarcinoma cell culture medium by the ExoTIC device (5 mL), ultracentrifugation (60 mL), and PEG (5 mL). (e) Mean size of EVs purified by the three methods as determined by NTA (NanoSight NS300). (f) Total quantity of EVs purified from different volumes of HCC827 cell culture medium using the ExoTIC device. (g) TEM image of EVs isolated from cell culture media (HCC827 cell line) using the ExoTIC device, immuno-gold labeled for CD63 (dark spots). (h) Demonstration of the ExoTIC device’s ability to isolate EVs from plasma volumes as low as 10 μL up to 500 μL. (i) Yield comparison between UC and ExoTIC device of EVs isolated from 500 μL of plasma from healthy human donors. Comparison of three different isolation methods with respect to (j) yield and (k) mean size (as determined by NTA) of EVs isolated from 100 μL plasma (mean ± SD, n = 5). Mean size refers to the average size of the EVs in the size distribution. Mean size values are automatically generated in the NanoSight report.