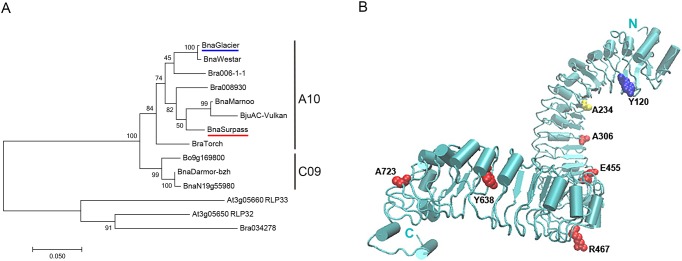
Fig 3. Phylogenetic tree and structural model of the leucine-rich repeat (LRR) domain of Brassica napus gene LepR3 for resistance against Leptosphaeria maculans.
(A) Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree of genes belonging to the LepR3/Rlm2 locus. Coding sequences were used to generate the tree. The Jukes-Cantor model [28] was used. The tree with the greatest log-likelihood is shown. Numbers indicate bootstrap values of 1,000 replicates. A discrete Gamma distribution was used to model evolutionary rate differences between sites. The rate variation model allowed for some sites to be evolutionarily invariable. Branch lengths are measured as the number of substitutions per site (scale bar). Branches designate species abbreviations: Bna = Brassica napus, Bra = B. rapa and Bju = B. juncea, followed by cultivar names or IDs, or accession numbers; BnaGlacier: AJG42078, BnaWestar: AJG42083, Bra 006-1-1: AJG42088, Bna-Marnoo: AJG42089, BjuAC-Vulkan: AJG42090, BnaSurpass: AGC13588, BraTorch: AJG42087. Gene IDs for genes that encode a receptor-like protein (RLP) are given after Arabidopsis thaliana accession numbers. Sequences from B. napus cultivars Glacier and Surpass, underlined in blue and red, respectively, have Rlm2 and LepR3 alleles, respectively, of the resistance gene on chromosome A10. Alleles identical to those from Glacier and Surpass were sequenced from three and two different cultivars, respectively. The sequence of cultivar Westar (no known R gene against L. maculans) was identical to sequences from eight other cultivars. (B) The modeled LRR domain starts at amino acid 27 and ends at amino acid 804. Seven amino acids predicted to be under positive selection are shown as vdW spheres. Residues in yellow (A234) and red (A306, E455, R467, Y638, A723) are supported at the 95% and 99% confidence level, respectively, using a comparison of 11 coding sequences. The residue in blue (Y120) is supported at the 95% level using four coding sequences.