Fig. 5.
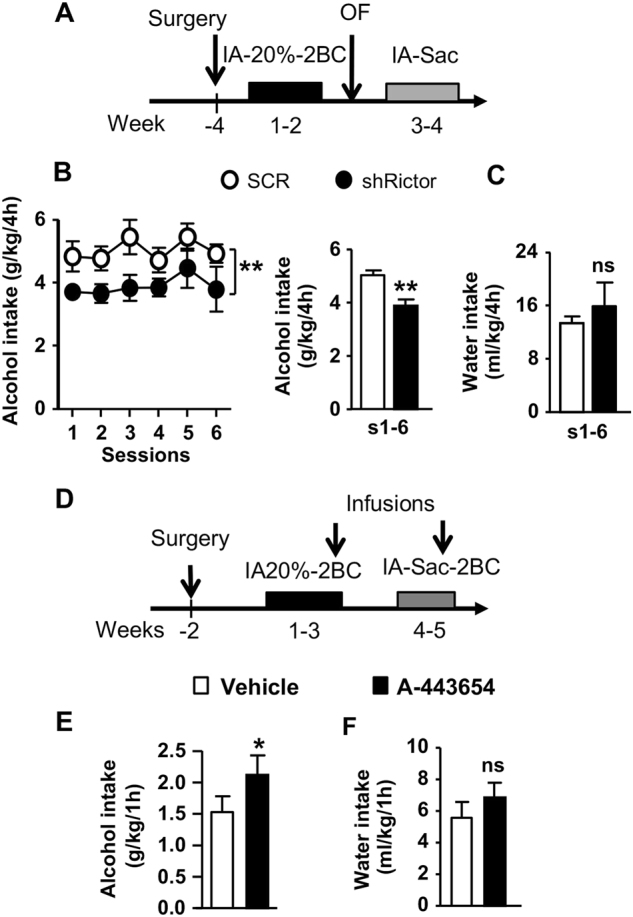
Downregulation of mTORC2 in the DMS reduces binge-like alcohol drinking whereas activation of mTORC2 promotes it. a Schematic representation of experimental timeline of experiment Mice were infused bilaterally with ltv-shRictor or ltv-SCR in the DMS. Four weeks later, animals underwent an IA20%-2BC for 6 sessions. Following 2 weeks of alcohol deprivation in which mice had access to water only, they were subjected to an IA0.01% sac for six sessions. Fluid intake was measured 4 h after the beginning of each drinking session. b, c Black circle and bar depicts ltv-shRictor and white circle and bar depicts ltv-SCR. b Alcohol intake (g/kg/4 h) across drinking sessions (left, main effect of virus F(1,13) = 14.18, p = 0.0024) and averaged (sessions 1 to 6) alcohol intake (right, t(13) = 3.77, p = 0.0024). c Water (ml/kg/4 h) intake on session 1 to 6 (s1–6) in the IA20%-2BC paradigm t(13) = 0.72, p = 0.484. d Schematic representation of timeline of experiment. Bilateral guide cannula were surgically implanted in the DMS. Two weeks later, mice underwent IA20%-2BC for 3 weeks and Vehicle or A-443654 (1 μg/μl) was infused in the DMS 15 min before the beginning of a drinking session. Fluid intake was measured 1 h after the beginning of the drinking session. Following 2 weeks of access to water only, mice were subjected to IA0.01% sac for 2 weeks prior to Vehicle or A-443654 (1 μg/μl) administration e Alcohol (g/kg/1 h) intake following intra-DMS infusion of vehicle (white) or A-443654 (black) t(8) = 2.38, p = 0.0449. f Water (ml/kg/1 h) intake t(8) = 1.23, p = 0.254. Data are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. b–c n = 7–8 per treatment, **p < 0.01 vs. ltv-SCR; e–f n = 9 per treatment, *p < 0.05 vs. vehicle
