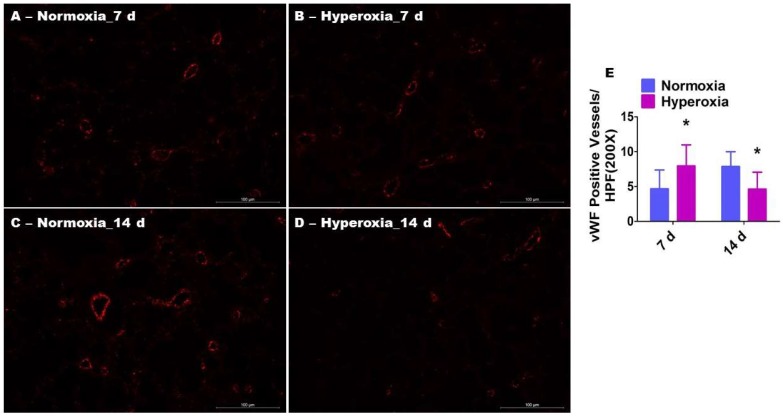
Figure 3.
Pulmonary vascularization in neonatal WT mice exposed to hyperoxia. One-day-old WT mice were exposed to either 21% O2 (normoxia) or 70% O2 (hyperoxia) for one or two weeks (n = 6/exposure/time-point), following which the lung sections were stained with anti-von Willebrand factor (vWF) antibodies. (A–D) Representative vWF-stained lung blood vessels (red). (E) Quantitative analysis of vWF-stained lung blood vessels per high-power field (HPF). The values are presented as the mean ± SD. Two-way ANOVA analysis showed an effect of hyperoxia and duration of exposure and an interaction between them for the dependent variable, vWF-stained vessels, in this figure. Significant differences between normoxia- and hyperoxia-exposed mice are indicated by * p < 0.01 (Two-way ANOVA). Scale bar = 100 µM.