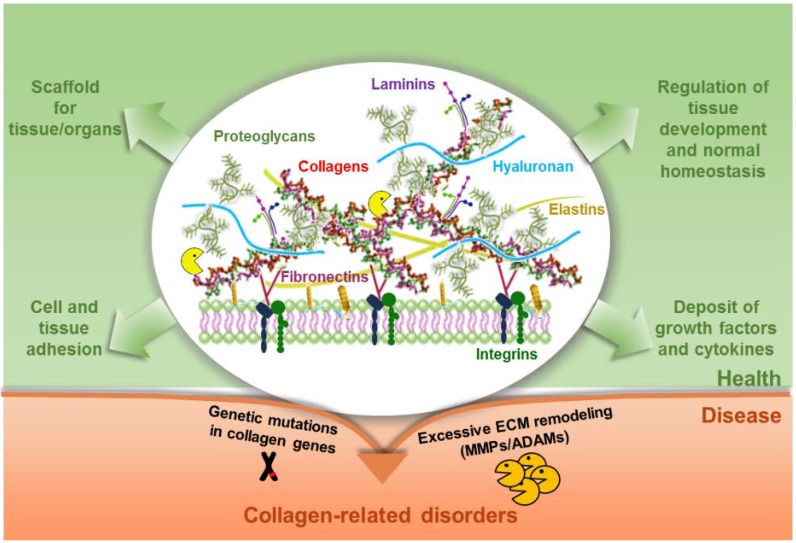
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the complex meshwork of proteins forming the extracellular matrix (ECM). The main ECM components, namely collagens, proteoglycans, hyaluronan, fibronectin, laminin and elastin, as well as the integrin ECM receptors, are depicted. The ECM provides mechanical support and anchoring for cells and tissues but it also acts as a reservoir of growth factors and cytokines and regulator of normal tissue development and homeostasis. Alterations in any of these functions result in a pathological status characterized by various tissue abnormalities.