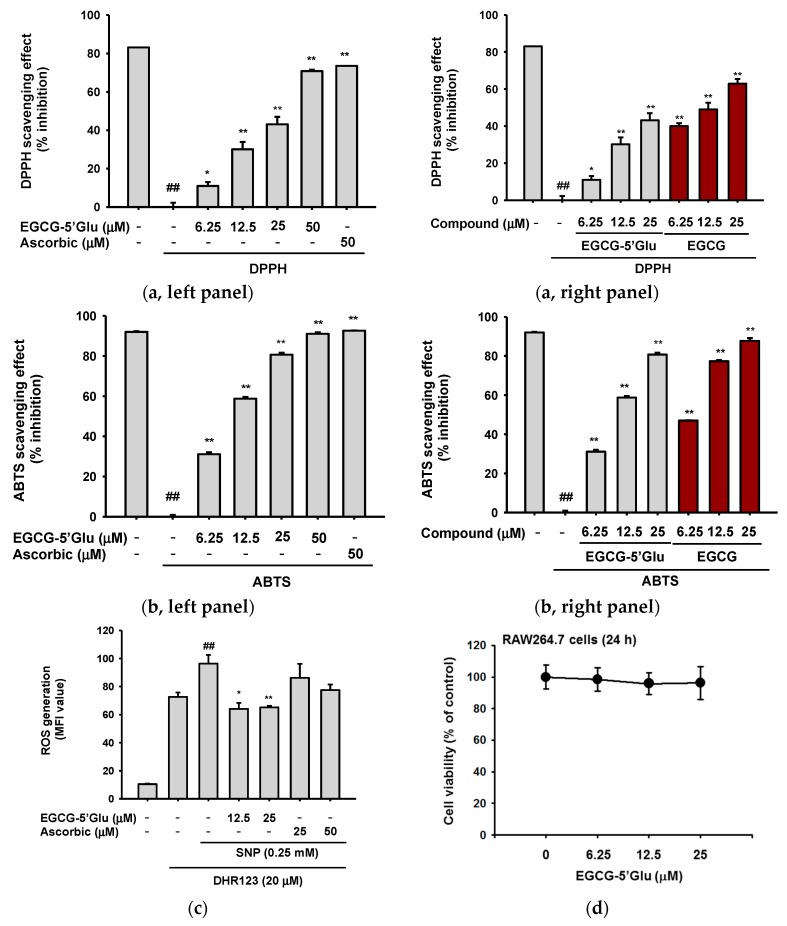
Figure 2.
Antioxidant effect of EGCG-5′Glu. 250 mM DPPH solution was incubated with EGCG-5′Glu (0–25 μM), ascorbic acid (50 μM) (a, left panel), or EGCG (0–25 μM) (a, right panel) at 37 °C for 30 min. Absorbance at 517 nm was measured by spectrophotometry. Ascorbic acid was used as a positive control. Mixture of 2,2'-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulphonic acid (ABTS) solution and EGCG-5′Glu (b, left panel) or EGCG (b, right panel) was reacted at 37 °C for 30 min. Scavenging of ABTS was determined by measuring absorbance at 730 nm. Ascorbic acid was used as positive control. (c) DHR123 was treated on RAW264.7 cells for 10 min, and EGCG-5′Glu or ascorbic acid were then added. Cells were incubated with sodium nitroprusside (SNP) for 20 min, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation was determined by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS). Ascorbic acid and EGCG were used for a positive control in DPPH assay, ABTS assay, and ROS generation experiment. (d) Cytotoxicity of EGCG-5′Glu on RAW264.7 cells was tested by MTT assay. ## p < 0.01 versus a normal group (untreated group), * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01 versus a control group (induced group).