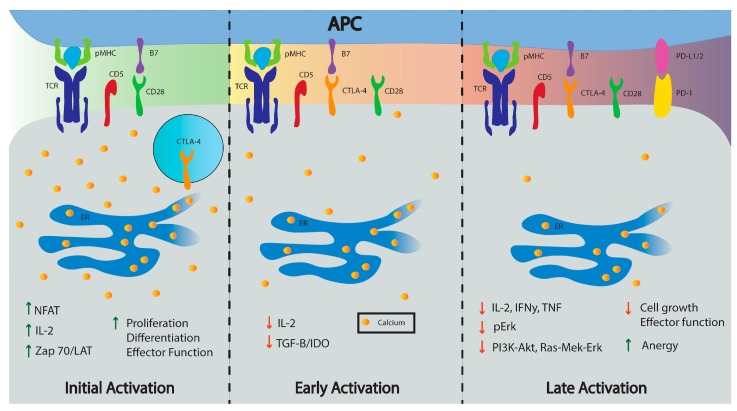
Figure 2.
Inhibiting co-receptors modulate T cell activation by increasing (green arrows) or decreasing activity (red arrows). CD5 is present in naïve T cells and localizes to the TCR:pMHC complex during activation. Initial activation cascades signal for the release of CTLA-4 from vesicles to the cell surface while the transcription factor NFAT transcribes PD-1. CTLA-4 provides inhibitory signals during early activation while PD-1 is expressed later and inhibits later stages of T cell activation. The initial Ca2+ mobilization is decreased by CTLA-4 and PD-1 downstream signals. A more detailed illustration of the calcium signaling pathway (i.e., IP3, STIM 1/2, CRAC channel, calmodulin, etc.) is outlined in Figure 3.