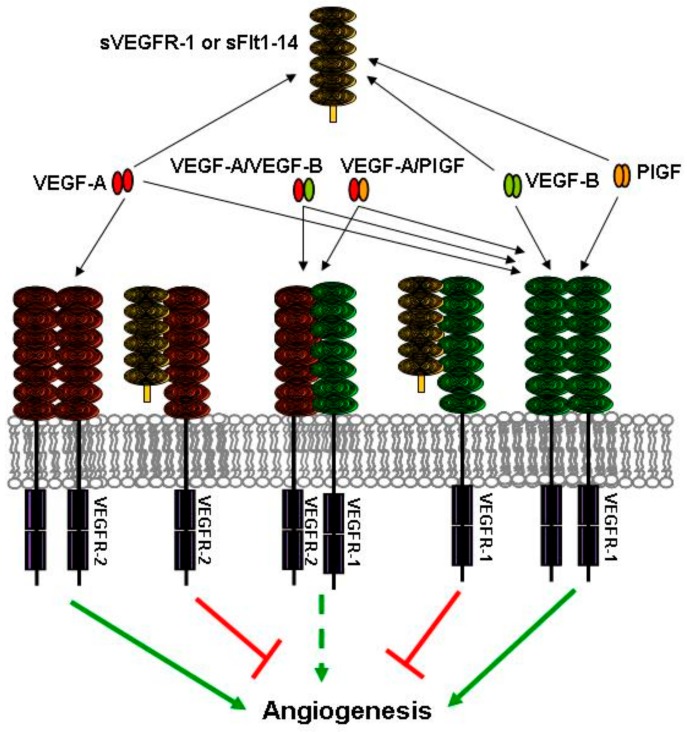
Figure 1.
Anti-angiogenic roles of soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR)-1 VEGFR-1 isoforms. Soluble VEGFR-1 isoforms, either sVEGFR-1 or soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase (sFlt)1-14, act as “VEGF sinks”. By binding members of the VEGF family, they decrease the amount of growth factors available to interact with the transmembrane tyrosine kinase receptors. In addition, soluble receptor isoforms can reduce VEGF signal transduction by binding to transmembrane receptor monomers and blocking formation of signaling competent receptor homodimers. Receptor heterodimers can also be inhibited by soluble isoforms, thus blocking the signaling of VEGF-A/placenta growth factor (PlGF) or VEGF-A/VEGF-B heterodimers. Interactions that lead to and hamper angiogenesis are indicated by green and red arrows/lines, respectively. The dashed arrow indicates the limited pro-angiogenic activity of receptor heterodimers.