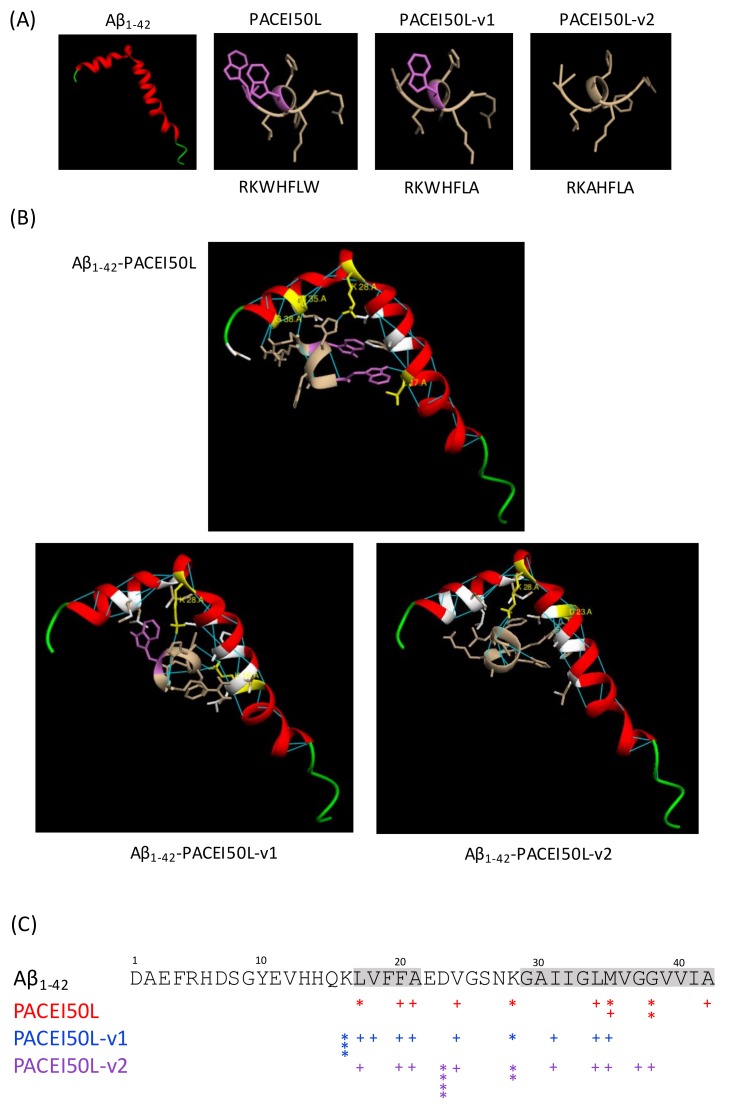
Figure 5.
The molecular docking model of the Aβ1–42 monomer binding to PACEI50L, PACEI50L-v1, and PACEI50L-v2. (A) The structure of Aβ1–42 (PDB, ID:1IYT), PACEI50L, PACEI50L-v1, and PACEI50L-v2; W residues are in purple. (B) PACEI50L is bound to Aβ1–42 via five intermolecular H-bonds with L17, K28, M35, and G38. PACEI50L-v1 is bound to Aβ1–42 via four H-bonds with K16 and K28. PACEI50L-v2 is bound via six intermolecular H-bonds with D23 and K28; Aβ1–42 residues participating in molecular interactions are in yellow (H bonds) and white (hydrophobic interactions); H-bonds are in blue. (C) A schematic representation of molecular interactions between Aβ1–42 and PACEI50L (red), PACEI50L-v1 (blue), and PACEI50L-v2 (purple); * intermolecular H-bond, + hydrophobic interaction, hydrophobic domains in Aβ1–42 are highlighted in grey.