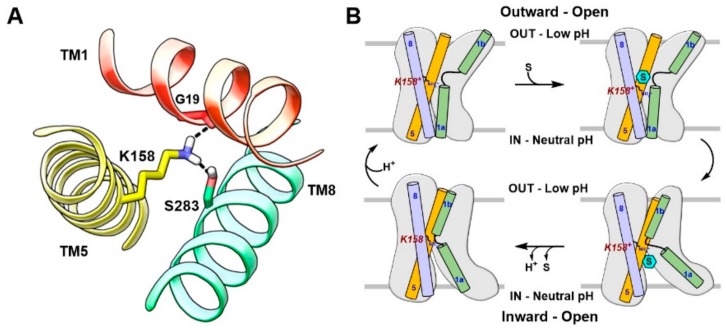
Figure 4.
(A) Hydrogen bond interactions of K158 (TM5) with G19 (TM1) and S283 (TM8) in ApcT (PDB ID: 3GI9) [40]; (B) Proposed mechanism of the conformational transition in ApcT. ApcT adopts an inward-open, occluded conformation when K158 is neutral (bottom left). An acidic pH stimulates the protonation of K158 leading to an outward-open state (top left). Upon substrate binding (top right), the transporter isomerizes to an inward-open state (bottom right). The formation of the inward-open, occluded conformation is preceded by the release of the substrate and proton(s) into the cytoplasm; (B) The figure was recreated from reference [40].